Researchers at Kyushu University and Vietnam's National Museum of Nature have discovered 16 new species of Loboscelidia, a strange-looking and elusive group of parasitoid wasps. The scientists also reported for the first time the unique parasitic behavior of a captive female of one species, Loboscelidia squamosa, who was observed digging a hole in the soil to hide her host's egg.
, smaller than a pencil-top eraser) and while unnoticed by humans, they play a crucial role in regulating the ecosystem.
"Loboscelidia was first discovered around 150 years ago, but we still lack important knowledge about their biology. This study was the first time we were able to observe their parasitic behavior," says first author, Dr. Yu Hisasue, formerly a Ph.D. student supervised by Mita. On one occasion, they trapped a living female from one of the newly described species, Loboscelidia squamosa. They released her into a plastic container containing soil and placed a stick insect egg inside. The female wasp punctured the egg, laid her own egg inside and then searched for a location to bury the parasitized egg. She used her head to dig a hole, placed the host egg inside and plugged the entrance with soil.
In total, the scientists identified 16 new species, bringing the known number of species worldwide up to 67.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 CERN researchers continue to look for elusive monopolesMagnetic monopoles are consistent with quantum mechanics and are called 'as one of the safest bets that one can make about physics not yet seen.”
CERN researchers continue to look for elusive monopolesMagnetic monopoles are consistent with quantum mechanics and are called 'as one of the safest bets that one can make about physics not yet seen.”
Read more »
 In major breakthrough, researchers close in on potential preeclampsia cureResearchers have achieved a significant breakthrough in identifying the primary cause and potential treatment for preeclampsia, a severe pregnancy complication. Experts pinpointed a toxic protein named cis P-tau in the blood and placenta of individuals with preeclampsia. The study describes cis P-tau as a pivotal circulating instigator of preeclampsia. An antibody developed in 2012 to target only the toxic protein while leaving its healthy counterpart unscathed is currently undergoing clinical trials in human patients suffering from traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer's Disease. The antibody has shown promising results in animal models and human cell cultures in treating the brain conditions. Upon testing this antibody in mice, the researchers found the all symptoms associated with preeclampsia were corrected.
In major breakthrough, researchers close in on potential preeclampsia cureResearchers have achieved a significant breakthrough in identifying the primary cause and potential treatment for preeclampsia, a severe pregnancy complication. Experts pinpointed a toxic protein named cis P-tau in the blood and placenta of individuals with preeclampsia. The study describes cis P-tau as a pivotal circulating instigator of preeclampsia. An antibody developed in 2012 to target only the toxic protein while leaving its healthy counterpart unscathed is currently undergoing clinical trials in human patients suffering from traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer's Disease. The antibody has shown promising results in animal models and human cell cultures in treating the brain conditions. Upon testing this antibody in mice, the researchers found the all symptoms associated with preeclampsia were corrected.
Read more »
 Researchers uncover unconventional charge carriers in a triangular-lattice Mott insulatorMott insulators are a peculiar class of materials with structures that should theoretically conduct electricity, but that are instead insulators. These materials contain strongly correlated electrons, which can generate highly entangled many-body states marked by unconventional excitations.
Researchers uncover unconventional charge carriers in a triangular-lattice Mott insulatorMott insulators are a peculiar class of materials with structures that should theoretically conduct electricity, but that are instead insulators. These materials contain strongly correlated electrons, which can generate highly entangled many-body states marked by unconventional excitations.
Read more »
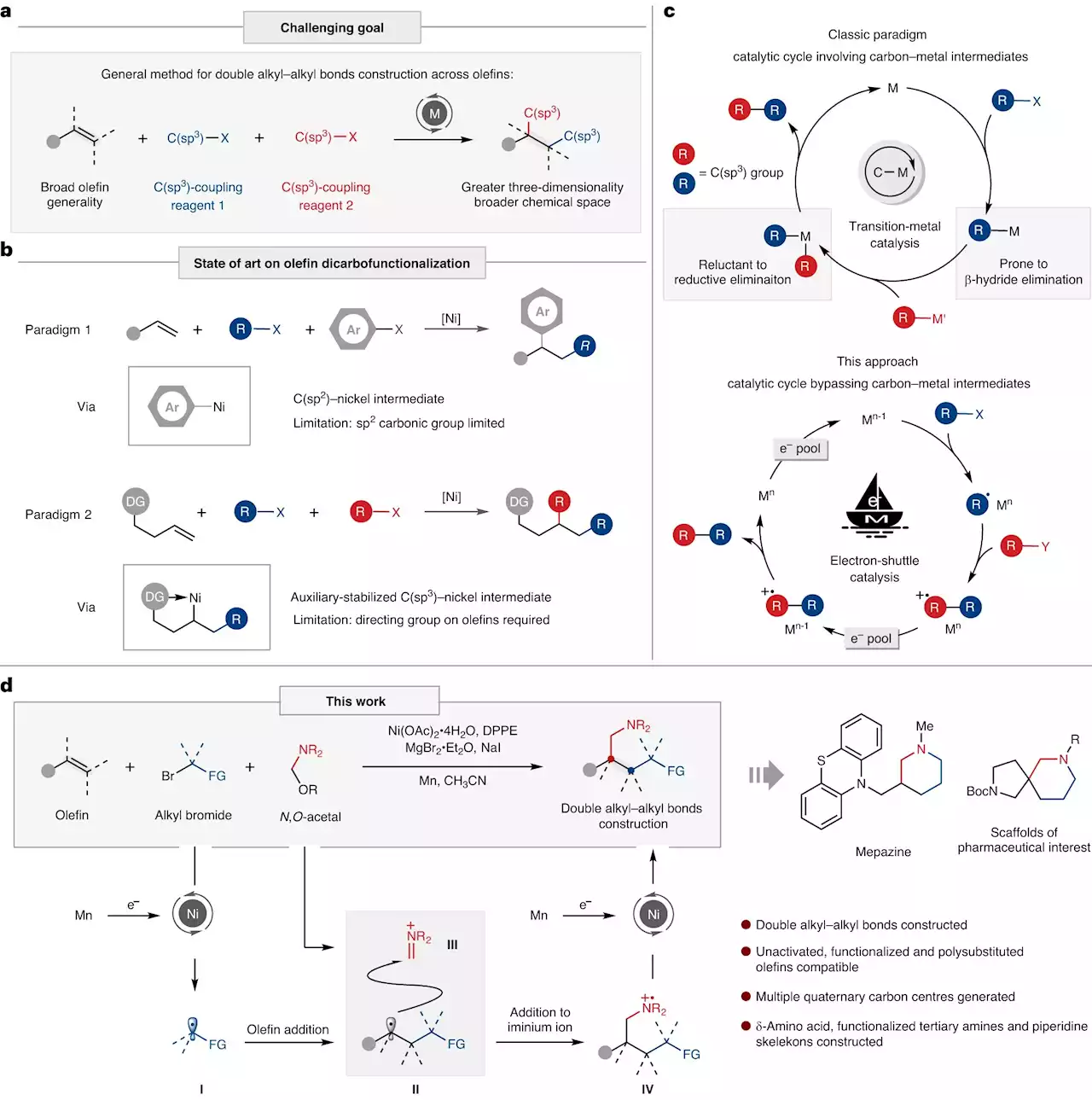 Researchers propose novel paradigm of metal electron-shuttle catalysisProfessor Huang Hanmin's research team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a new paradigm of metal electron-shuttle catalysis, which has been pioneeringly employed to achieve alkylative aminomethylation of unactivated alkene for the first time. Their work was published in Nature Catalysis on August 21.
Researchers propose novel paradigm of metal electron-shuttle catalysisProfessor Huang Hanmin's research team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a new paradigm of metal electron-shuttle catalysis, which has been pioneeringly employed to achieve alkylative aminomethylation of unactivated alkene for the first time. Their work was published in Nature Catalysis on August 21.
Read more »
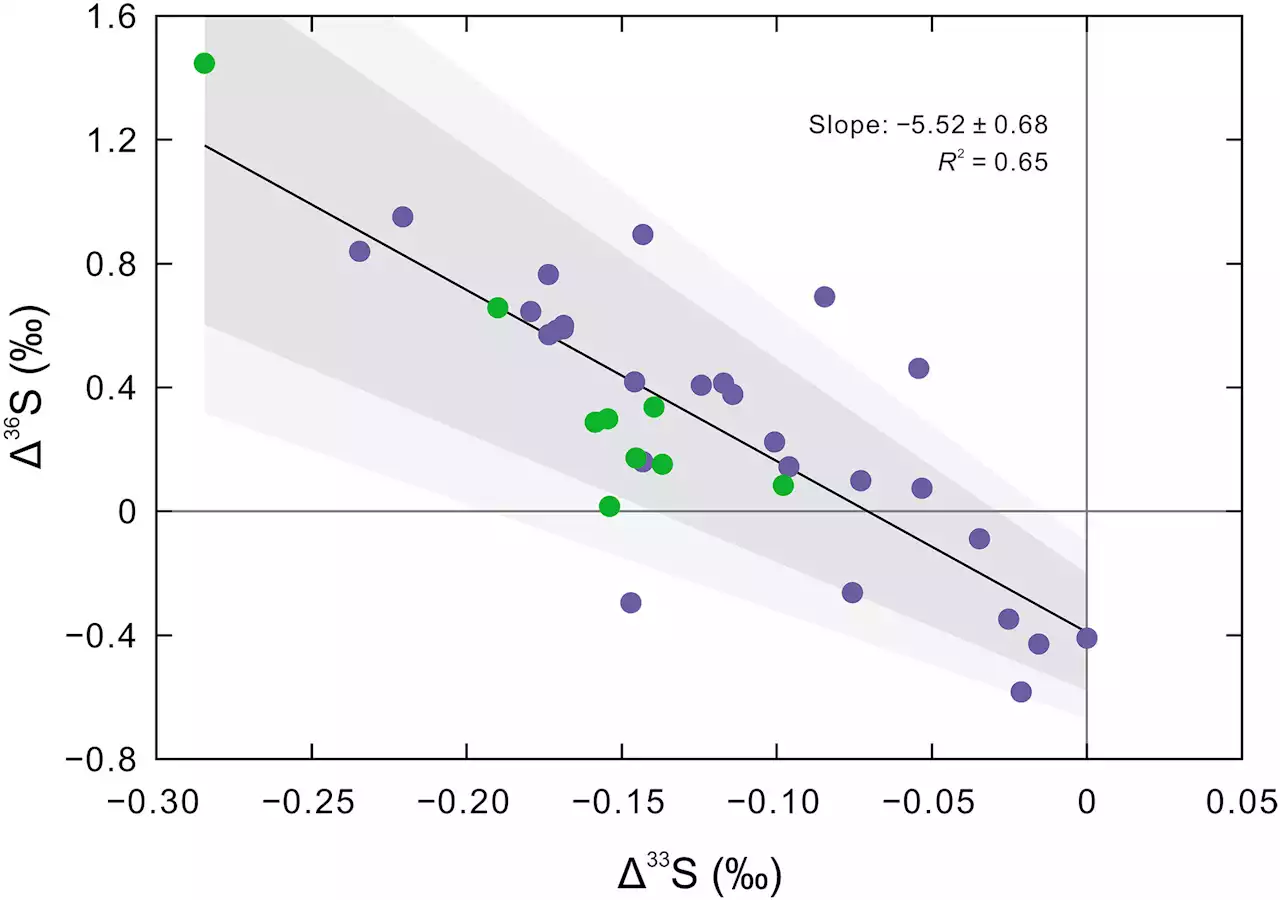 Researchers illuminate 'Snowball Earth' melting and early life evolutionA research team led by Prof. Shen Yan'an from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) conducted a systematic study of the interglacial stratigraphy in South China by means of high-precision sulfur and mercury isotope analyses.
Researchers illuminate 'Snowball Earth' melting and early life evolutionA research team led by Prof. Shen Yan'an from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) conducted a systematic study of the interglacial stratigraphy in South China by means of high-precision sulfur and mercury isotope analyses.
Read more »
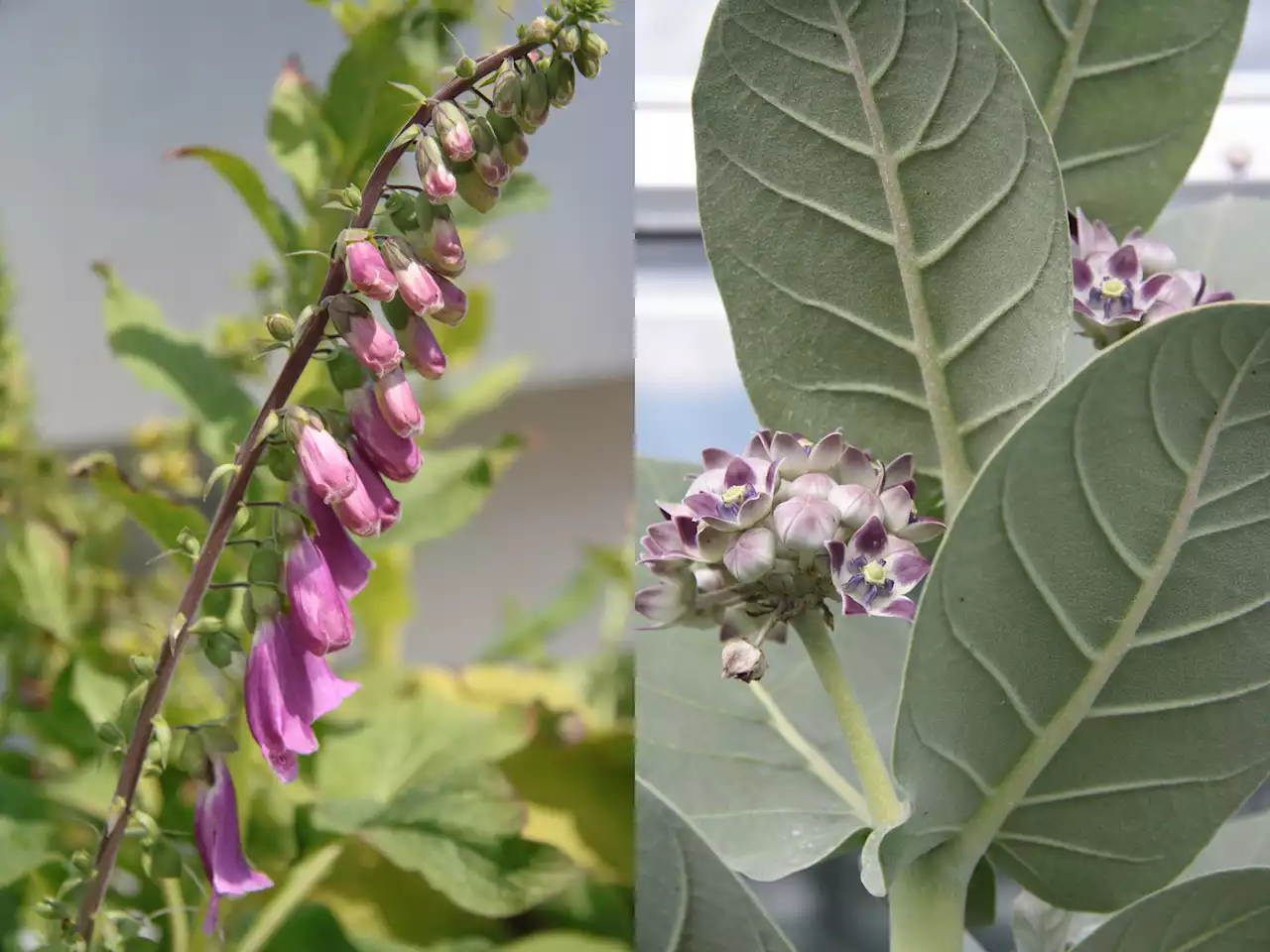 Researchers study the formation of cardenolides in plantsScientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena are investigating the previously largely unknown biosynthetic pathway that leads to the formation of cardenolides in plants.
Researchers study the formation of cardenolides in plantsScientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena are investigating the previously largely unknown biosynthetic pathway that leads to the formation of cardenolides in plants.
Read more »
