Study reveals why immunotherapies don't work on hardest-to-treat breast cancers naturecancer
Boxes show three individual areas that have been and expanded, with indicated channels separated. Arrowheads mark p21 + /CD80 + and IRF1 + /PD-L1+ cells ; γH2AX + /CD80+ cells and γH2AX/PD-L1 negative cells ; p-Stat3+/PD-L1+ and p-Stat3 + /CD80+ cells .Untreated tumor stained and imaged in parallel. Scale bar=40 µm. qPCR and IF were repeated at least twice and representative data are shown.
CRISPR-Cas9 was used to generate a p53 knockout clone and a non-edited control of 4226 cell line.p53 knockout clone 2 of the 4226 cell line was untreated or treated with doxorubicin as indicated. Over 1 to 5 days, these cultures were then exposed to rIFNγ for 24 h ) or not , followed by immunoblot for CD80, PD-L1, Stat1, and IRF1 on a total of 2 membranes, which were then blotted for actin.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 FDA approves AI-powered breast cancer screening toolBreast cancer screening AI app OK'd by watchdog
FDA approves AI-powered breast cancer screening toolBreast cancer screening AI app OK'd by watchdog
Read more »
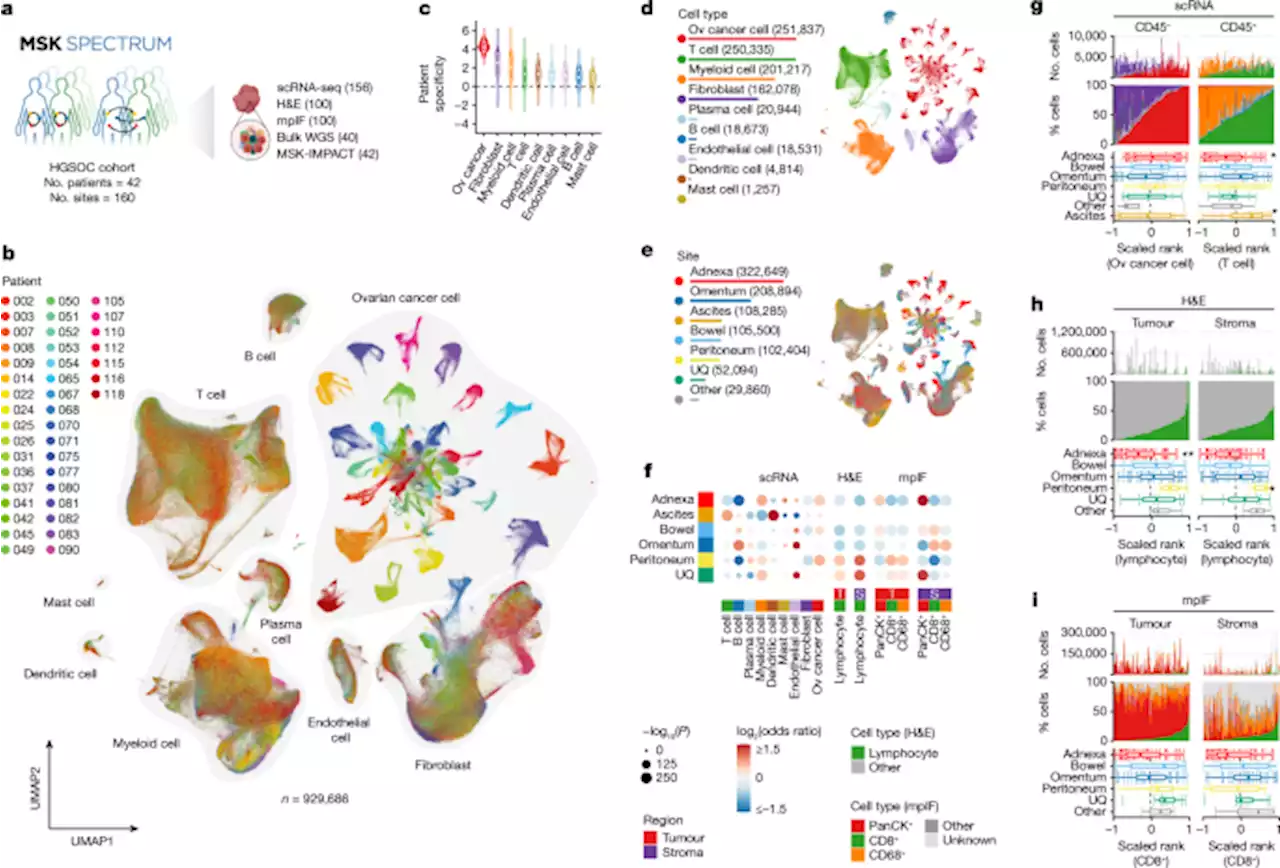 Ovarian cancer mutational processes drive site-specific immune evasion - NatureMulti-modal analysis of genomically unstable ovarian tumours characterizes the contribution of anatomical sites and mutational processes to evolutionary phenotypic divergence and immune resistance mechanisms.
Ovarian cancer mutational processes drive site-specific immune evasion - NatureMulti-modal analysis of genomically unstable ovarian tumours characterizes the contribution of anatomical sites and mutational processes to evolutionary phenotypic divergence and immune resistance mechanisms.
Read more »
 Phosphoproteomic analysis of neoadjuvant breast cancer suggests that increased sensitivity to paclitaxel is driven by CDK4 and filamin A - Nature CommunicationsPhosphoproteomics is a promising tool for identifying biomarkers of treatment response in cancer. Here, the authors analyse proteomics profiling of HER2-negative female breast cancer patients and identify potential predictors of paclitaxel response.
Phosphoproteomic analysis of neoadjuvant breast cancer suggests that increased sensitivity to paclitaxel is driven by CDK4 and filamin A - Nature CommunicationsPhosphoproteomics is a promising tool for identifying biomarkers of treatment response in cancer. Here, the authors analyse proteomics profiling of HER2-negative female breast cancer patients and identify potential predictors of paclitaxel response.
Read more »
 Biodiversity: Can we set aside a third of our planet for nature?Will a plan to protect 30% of the planet for nature by 2030 be agreed and how will it work?
Biodiversity: Can we set aside a third of our planet for nature?Will a plan to protect 30% of the planet for nature by 2030 be agreed and how will it work?
Read more »
 Manchester's Kenworthy Woods: Former tip declared nature reserveKenworthy Woods, which was transformed in the 1990s, becomes Manchester's ninth local nature reserve
Manchester's Kenworthy Woods: Former tip declared nature reserveKenworthy Woods, which was transformed in the 1990s, becomes Manchester's ninth local nature reserve
Read more »
 Pathogenic variants in SLF2 and SMC5 cause segmented chromosomes and mosaic variegated hyperploidy - Nature CommunicationsThe SMC5/6 complex is critical for genome stability. Here, the authors identify mutations in SLF2 and SMC5 as cause of Atelís Syndrome characterized by microcephaly, short stature, anemia, segmented chromosomes and mosaic variegated hyperploidy.
Pathogenic variants in SLF2 and SMC5 cause segmented chromosomes and mosaic variegated hyperploidy - Nature CommunicationsThe SMC5/6 complex is critical for genome stability. Here, the authors identify mutations in SLF2 and SMC5 as cause of Atelís Syndrome characterized by microcephaly, short stature, anemia, segmented chromosomes and mosaic variegated hyperploidy.
Read more »
