Epitope mapping reveals the humoral responses against the main SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins in infected patients from Africa SciReports PasteurDakar HESAM_Univ pasteurMG epitope SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid
By Neha MathurJan 18 2023Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc. In a recent article published in Scientific Reports, researchers performed immunoglobulin M and IgG epitope mapping against 487 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 peptides. These peptides encompassed four main structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2, viz., spike glycoprotein, envelope , nucleocapsid , and membrane proteins.
The study population comprised 65 and 16 SARS-CoV-2-infected patients and 32 and 10 uninfected individuals from Senegal and Madagascar, respectively. The researchers collected serum samples from these two groups and assessed whether their varying IgM and IgG epitope distributions explained their different COVID-19 clinical profiles. Further, they compared the results with previous studies from Europe, Asia, and the United States of America .
Antibodies eBook Compilation of the top interviews, articles, and news in the last year. Download a free copy Furthermore, the observed humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 in people from Madagascar and Senegal were quite comparable, with some differences due to varying patient profiles at sampling time. Samples belonged to patients with early or late-stage SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Overall patterns of SARS-CoV-2 caused by variants of concern among children and adolescentsOverall patterns of SARS-CoV-2 caused by variants of concern among children and adolescents medrxivpreprint UniBasel_en unibern institutpasteur sheffielduni SARSCoV2 covid coronavirus covid variantsofconcern childhealth teenagers
Overall patterns of SARS-CoV-2 caused by variants of concern among children and adolescentsOverall patterns of SARS-CoV-2 caused by variants of concern among children and adolescents medrxivpreprint UniBasel_en unibern institutpasteur sheffielduni SARSCoV2 covid coronavirus covid variantsofconcern childhealth teenagers
Read more »
Haemorrhage of human foetal cortex associated with SARS-CoV-2 infectionMassimo et al. report the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in first and second trimester foetal brain tissue in association with cortical haemorrhages. The haemorrhages w
Read more »
 The 'Great Escape' by SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1In a recent article published in the Lancet Microbe, researchers in the Netherlands and the United Kingdom quantified the antigenic diversity of new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) subvariants, BQ.1.1, BM.1.1.1, and XBB.1, all derivatives of the variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, which emerged in late 2022.
The 'Great Escape' by SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1In a recent article published in the Lancet Microbe, researchers in the Netherlands and the United Kingdom quantified the antigenic diversity of new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) subvariants, BQ.1.1, BM.1.1.1, and XBB.1, all derivatives of the variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, which emerged in late 2022.
Read more »
 Tight transmission bottlenecks may limit the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 variantsA new study describes that tight transmission bottlenecks restrict the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in the transmission chain. SARS-CoV-2 is the causative pathogen of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Tight transmission bottlenecks may limit the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 variantsA new study describes that tight transmission bottlenecks restrict the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in the transmission chain. SARS-CoV-2 is the causative pathogen of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read more »
 S. aureus enhances replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro through the bacterial iron-regulated surface determinant protein AS. aureus enhances replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro through the bacterial iron-regulated surface determinant protein A WesternU SARSCoV2 bacteria virus covid coronavirus covid
S. aureus enhances replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro through the bacterial iron-regulated surface determinant protein AS. aureus enhances replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro through the bacterial iron-regulated surface determinant protein A WesternU SARSCoV2 bacteria virus covid coronavirus covid
Read more »
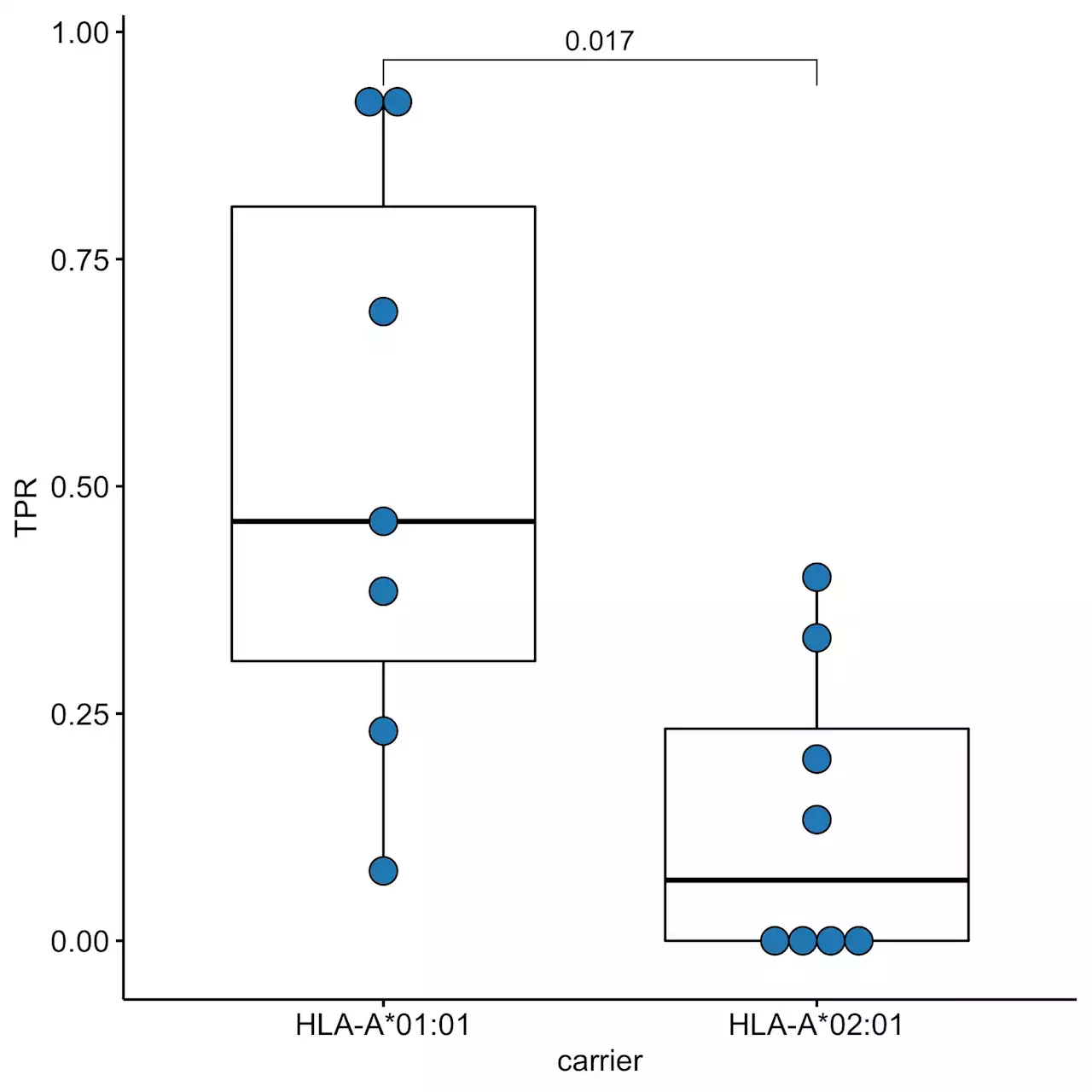 Researchers reveal genetic predisposition to immunity against new variants of COVID-19The SARS-CoV-2 delta variant that caused the third wave of COVID-19 in mid-2021 turned out to be more contagious than earlier SARS-CoV-2 variants. In addition, protein mutations in the delta variant were found to significantly reduce the effect of acquired humoral immunity to COVID-19 from prior infection or vaccination.
Researchers reveal genetic predisposition to immunity against new variants of COVID-19The SARS-CoV-2 delta variant that caused the third wave of COVID-19 in mid-2021 turned out to be more contagious than earlier SARS-CoV-2 variants. In addition, protein mutations in the delta variant were found to significantly reduce the effect of acquired humoral immunity to COVID-19 from prior infection or vaccination.
Read more »
