Researchers elucidated monkeypox's (mpox) epidemiological and clinical features.
By Vijay Kumar MalesuSep 8 2023Reviewed by Lily Ramsey, LLM In a recent study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases, researchers elucidated monkeypox's epidemiological and clinical features in individuals with a history of infection or vaccination, enhancing the understanding of disease behavior before immunity.
Concerns exist regarding the effectiveness and duration of immunity post-vaccination or following previous infection. Although the PHEIC declaration ended in May 2023, the ongoing transmission of the Clade IIb strain of mpox in humans suggests the potential for future outbreaks. To be considered a confirmed mpox case post-infection, a patient had to display clinical signs and possess a polymerase chain reaction --confirmed infection history, followed by recovery.
Initial findings indicated its efficacy in gauging the disease's severity and tracking its progression. The median age of the participants was 36 years, the majority being White, cis-gendered gay or bisexual men. Interestingly, most reported having multiple male partners and inconsistent condom use, with eight individuals having HIV, all of whom were under effective antiretroviral therapy.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers characterize new SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 variant neutralization by monoclonal antibodiesResearchers used a SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-pseudotyped viral model to characterize BA.2.86 variant neutralization by monoclonal antibodies.
Researchers characterize new SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 variant neutralization by monoclonal antibodiesResearchers used a SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-pseudotyped viral model to characterize BA.2.86 variant neutralization by monoclonal antibodies.
Read more »
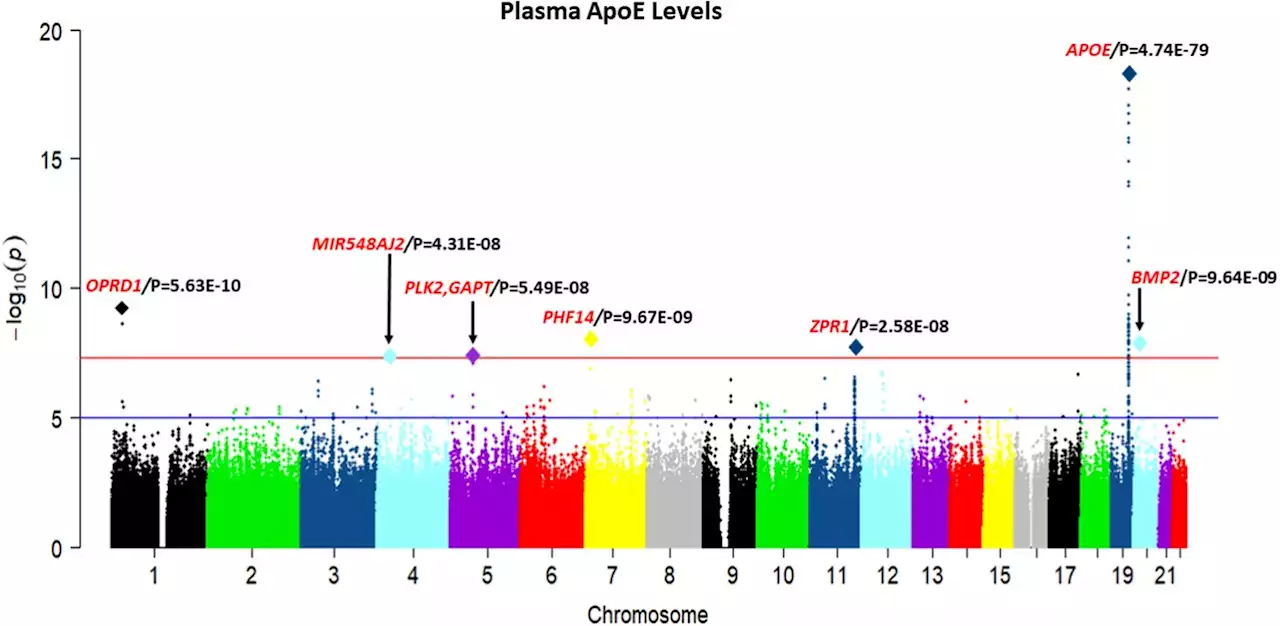 Researchers uncover new genetic traits influencing Alzheimer's riskResearchers at the University of Pittsburgh analyzed thousands of human genomes to find new gene variations responsible for controlling the levels of blood plasma molecules linked to Alzheimer's disease risk. The findings, published recently in Molecular Psychiatry, could contribute to the future development of simple blood tests for the disease.
Researchers uncover new genetic traits influencing Alzheimer's riskResearchers at the University of Pittsburgh analyzed thousands of human genomes to find new gene variations responsible for controlling the levels of blood plasma molecules linked to Alzheimer's disease risk. The findings, published recently in Molecular Psychiatry, could contribute to the future development of simple blood tests for the disease.
Read more »
 Researchers identify new gene mutation that alters Alzheimer's disease riskA study led by experts from Indiana University School of Medicine has shed new light on the genetic underpinnings of Alzheimer's disease. The team's research, rooted in human genetics studies, has unearthed a critical mutation within a key gene operating in the brain's immune cells, potentially elevating the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Researchers identify new gene mutation that alters Alzheimer's disease riskA study led by experts from Indiana University School of Medicine has shed new light on the genetic underpinnings of Alzheimer's disease. The team's research, rooted in human genetics studies, has unearthed a critical mutation within a key gene operating in the brain's immune cells, potentially elevating the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Read more »
 Researchers find that pressure in the biliary system leads to tissue changes in the liverThe liver produces bile, which the intestine uses for digestion. For the transport of bile, the liver relies on a network of microscopic tubings, known as bile canaliculi, formed by liver cells called hepatocytes. When the outflow of bile to the intestine is blocked, it collects in the liver and can lead to serious liver disease.
Researchers find that pressure in the biliary system leads to tissue changes in the liverThe liver produces bile, which the intestine uses for digestion. For the transport of bile, the liver relies on a network of microscopic tubings, known as bile canaliculi, formed by liver cells called hepatocytes. When the outflow of bile to the intestine is blocked, it collects in the liver and can lead to serious liver disease.
Read more »
 Researchers take major step towards creating synthetic embryo-like structures that mimic real human embryosThe aim of the research is not to create synthetic, or artificial life, but to produce working models that will allow scientists to study crucial stages in human development.
Researchers take major step towards creating synthetic embryo-like structures that mimic real human embryosThe aim of the research is not to create synthetic, or artificial life, but to produce working models that will allow scientists to study crucial stages in human development.
Read more »
 Rare and dazzling cosmic explosion spotted by researchersThe explosion, which outshines most supernovae in the universe, was spotted by researchers at the Queen’s University, Belfast.
Rare and dazzling cosmic explosion spotted by researchersThe explosion, which outshines most supernovae in the universe, was spotted by researchers at the Queen’s University, Belfast.
Read more »
