Forecast: There’s a 100% chance of recurring two-sided jets for a pair of stars that are actively gathering mass. Like kittens, actively forming stars are balls of energy. But instead of being overtaken by the zoomies, stars emit energy in the form of jets, creating fantastic, textured scenes. That
These stars have a lot of energy to let loose! NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured a tightly bound pair of actively forming stars, known as Herbig-Haro 46/47, in high-resolution near-infrared light. Look for them at the center of the red diffraction spikes. The stars are buried deeply, appearing as an orange-white splotch. They are surrounded by a disk of gas and dust that continues to add to their mass. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph DePasquale , Anton M.
Six near-infrared images from NIRCam aboard the James Webb Space Telescope make up this composite of Herbig-Haro 46/47. The scale bar is labeled in arcminutes, which is a measure of angular distance on the sky. One arcminute is equal an angular measurement equal to 1/60 of one degree. The actual size of an object that covers one arcminute on the sky depends on its distance from the telescope.Webb Space Telescope Snaps Highly Detailed Infrared Image of Actively Forming Starshas captured the “antics” of a pair of actively forming young stars, known as Herbig-Haro 46/47, in high-resolution near-infrared light.
The stars’ more recent ejections appear in a thread-like blue. They run just below the red horizontal diffraction spike at 2 o’clock. Along the right side, these ejections make clearer wavy patterns. They are disconnected at points, and end in a remarkable uneven light purple circle in the thickest orange area. Lighter blue, curly lines also emerge on the left, near the central stars, but are sometimes overshadowed by the bright red diffraction spike.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
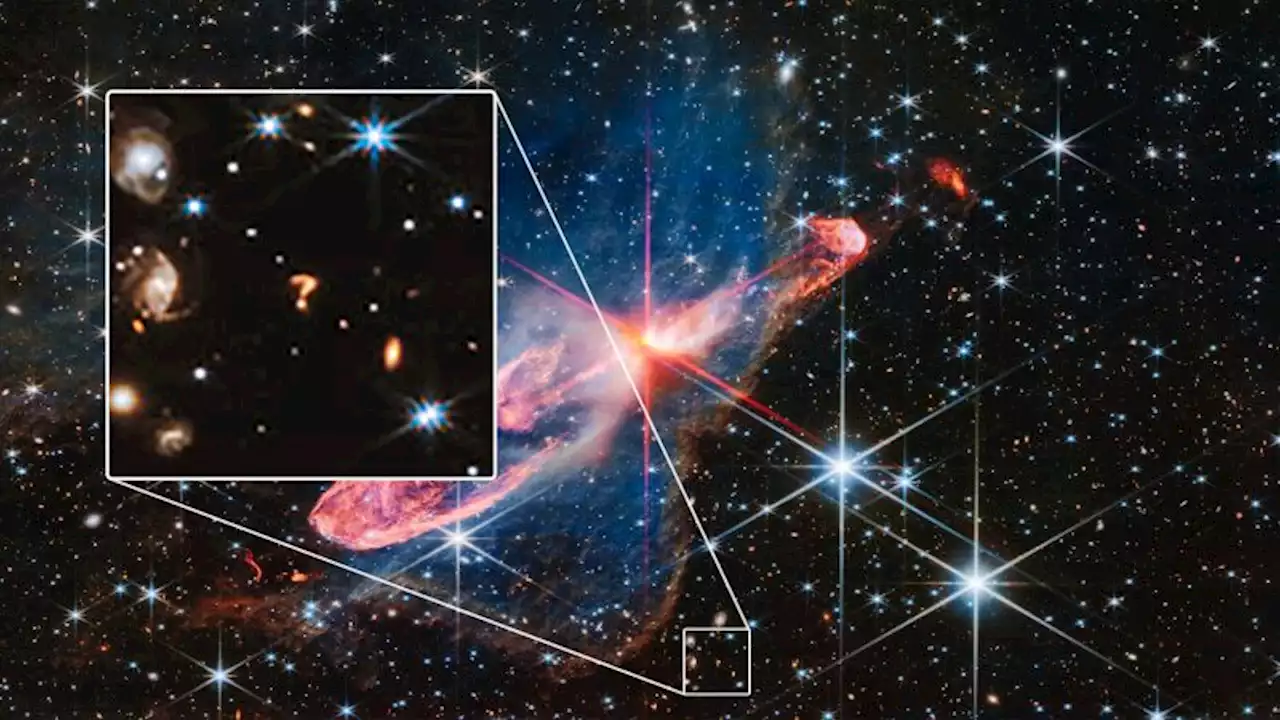 Webb telescope spots cosmic question mark in spaceA cosmic object in the shape of a glowing question mark has photobombed one of the latest images captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope — and scientists think they know what it might be
Webb telescope spots cosmic question mark in spaceA cosmic object in the shape of a glowing question mark has photobombed one of the latest images captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope — and scientists think they know what it might be
Read more »
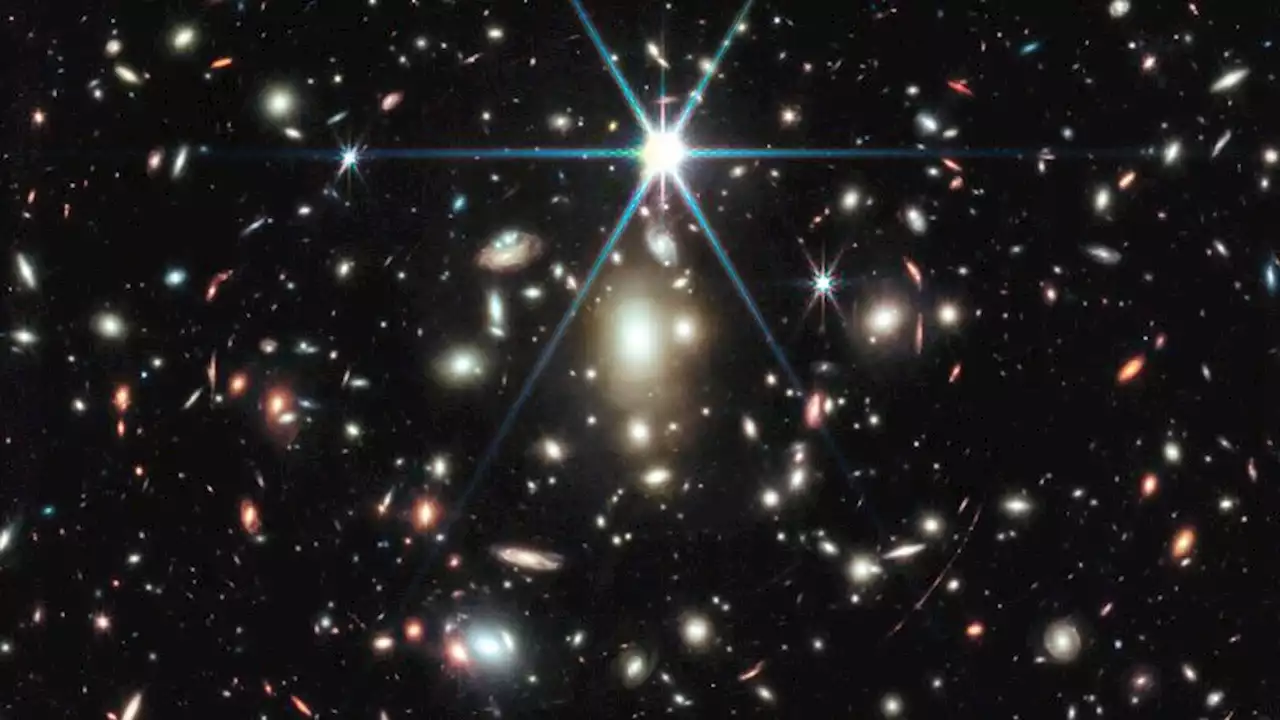 Webb telescope captures image of most distant star ever seenThe James Webb Space Telescope has been used to observe Earendel, the most distant star ever detected.
Webb telescope captures image of most distant star ever seenThe James Webb Space Telescope has been used to observe Earendel, the most distant star ever detected.
Read more »
 Galaxy Spotted By Webb Space Telescope is One of the Earliest Ever SeenFollow-up observations of a distant galaxy suggest its age is about 13.4 billion years.
Galaxy Spotted By Webb Space Telescope is One of the Earliest Ever SeenFollow-up observations of a distant galaxy suggest its age is about 13.4 billion years.
Read more »
 Astronomers confirm Maisie’s galaxy is one of the oldest observedAstronomers have used advanced instruments to calculate a more accurate age of Maisie’s galaxy, discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in June 2022.
Astronomers confirm Maisie’s galaxy is one of the oldest observedAstronomers have used advanced instruments to calculate a more accurate age of Maisie’s galaxy, discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in June 2022.
Read more »
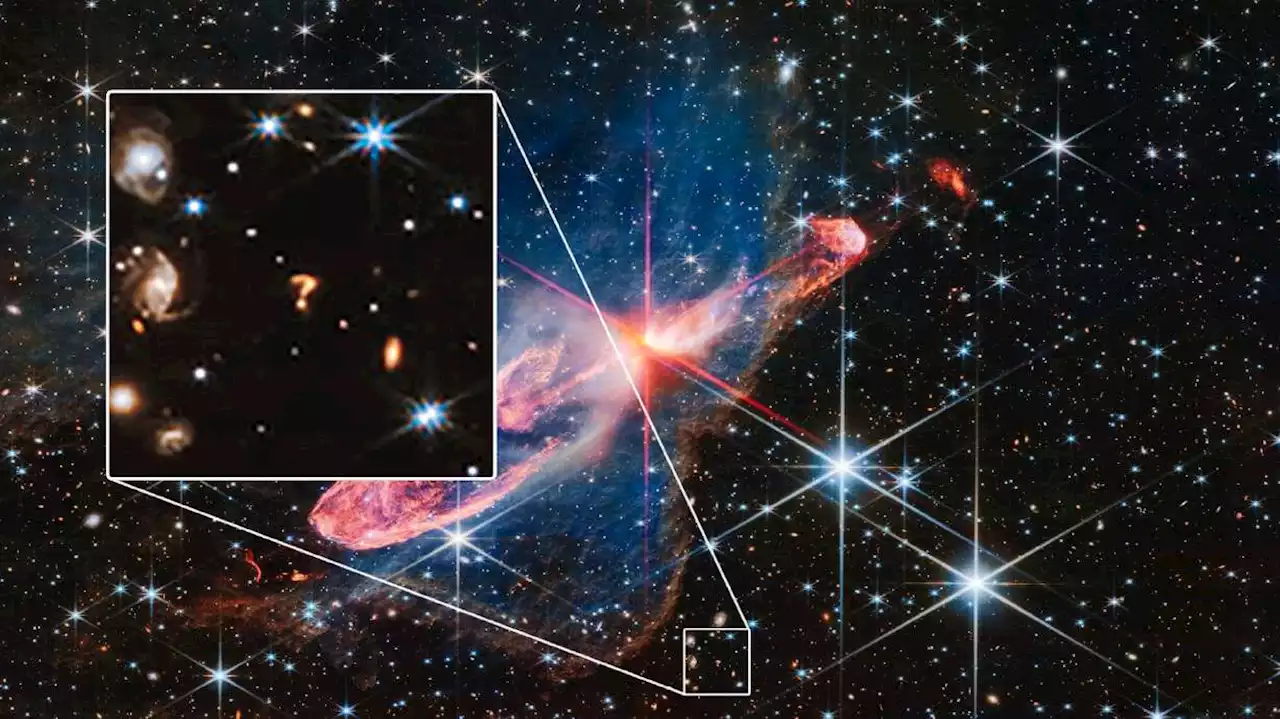 NASA telescope spots cosmic question mark in deep spaceA cosmic object in the shape of a glowing question mark has photobombed one of the latest images captured by NASA's James Webb Space Telescope — and scientists think they know what it might be.
NASA telescope spots cosmic question mark in deep spaceA cosmic object in the shape of a glowing question mark has photobombed one of the latest images captured by NASA's James Webb Space Telescope — and scientists think they know what it might be.
Read more »
