Nanospacecraft Helps Cancer Therapies Land on Specific Target ACS_AMI
By Dr. Priyom Bose, Ph.D.Oct 6 2022Reviewed by Megan Craig, M.Sc. Conventional chemotherapeutics kill both cancerous and healthy cells and cause several side effects in patients. The negative effects limit the maximum tolerated drug dose, compromising its optimal therapeutic efficacy.
Limitations of Conventional Chemotherapeutics for Cancer Therapy In the past few decades, conventional chemotherapeutics have been used as the first line of standard treatment for a wide range of malignancies. One of the commonly used drugs is doxorubicin , which exhibited desirable therapeutic efficacy against malignancies. Mechanistically, this drug interferes with nucleic acid synthesis in cancerous cells.
Several human cancers have been linked with mitochondrial dysfunctions, such as insensitivity to anti-growth signals, uncontrolled cell proliferation, decreased autophagy, and enhanced anabolism. The malignant properties of cancer cells are associated with a high reactive oxygen species level, which can promote drug resistance. Recently, mitochondria have been considered to be a potential target for anticancer drugs, including Dox.
Although nanocarriers can target tumor cells, the majority of them cannot transport antitumor drugs into subcellular organelles . To overcome this limitation, there is a need to develop a targeted drug-delivery system that can deliver anticancer therapeutics into specific cellular organelles. GM-NSC is a nanocomposite containing Au-NPs, surrounded by dense multilayers of DNA crowns that are self-assembled from DNA tetra in an orderly fashion. Each tetrahedral DNA structural unit was equipped with three functional components, namely, a hidden mitochondria-targeting triphenylphosphonium , an explosive bolt , and a cancer cell-targeting aptamer pointing toward the outer environment. E-bolt has been assembled from the Lock strand, DNAzyme, and cleavage substrate.
Dox-loaded GM modified with TPP was able to precisely penetrate mitochondria and promote the mitochondrial accumulation of Dox, which ultimately damaged mitochondria by ROS generation and lowering of mitochondrial membrane potential. Subsequently, cytochrome c was released into the cytoplasm, which activated apoptosis-related enzymes caspase-9 and caspase-3. These activated enzymes triggered a cascade of molecular events causing tumor cell apoptosis.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Kate Garraway recently discovered she has a VERY famous relativeKate Garraway made the discovery while taking part in ITV's DNA Journey.
Kate Garraway recently discovered she has a VERY famous relativeKate Garraway made the discovery while taking part in ITV's DNA Journey.
Read more »
 DNA from skeletons reveals where first people to call themselves English came fromWhile the DNA analysis has challenged the understanding of ancient England as a whole, it also revealed a number of 'striking' individual stories.
DNA from skeletons reveals where first people to call themselves English came fromWhile the DNA analysis has challenged the understanding of ancient England as a whole, it also revealed a number of 'striking' individual stories.
Read more »
 Red Bull commence talks with Honda over possible F1 reunionHelmut Marko says Red Bull and Honda are in talks over a reunion, but as was the stance with Porsche, respecting Red Bull's 'DNA' is key.
Red Bull commence talks with Honda over possible F1 reunionHelmut Marko says Red Bull and Honda are in talks over a reunion, but as was the stance with Porsche, respecting Red Bull's 'DNA' is key.
Read more »
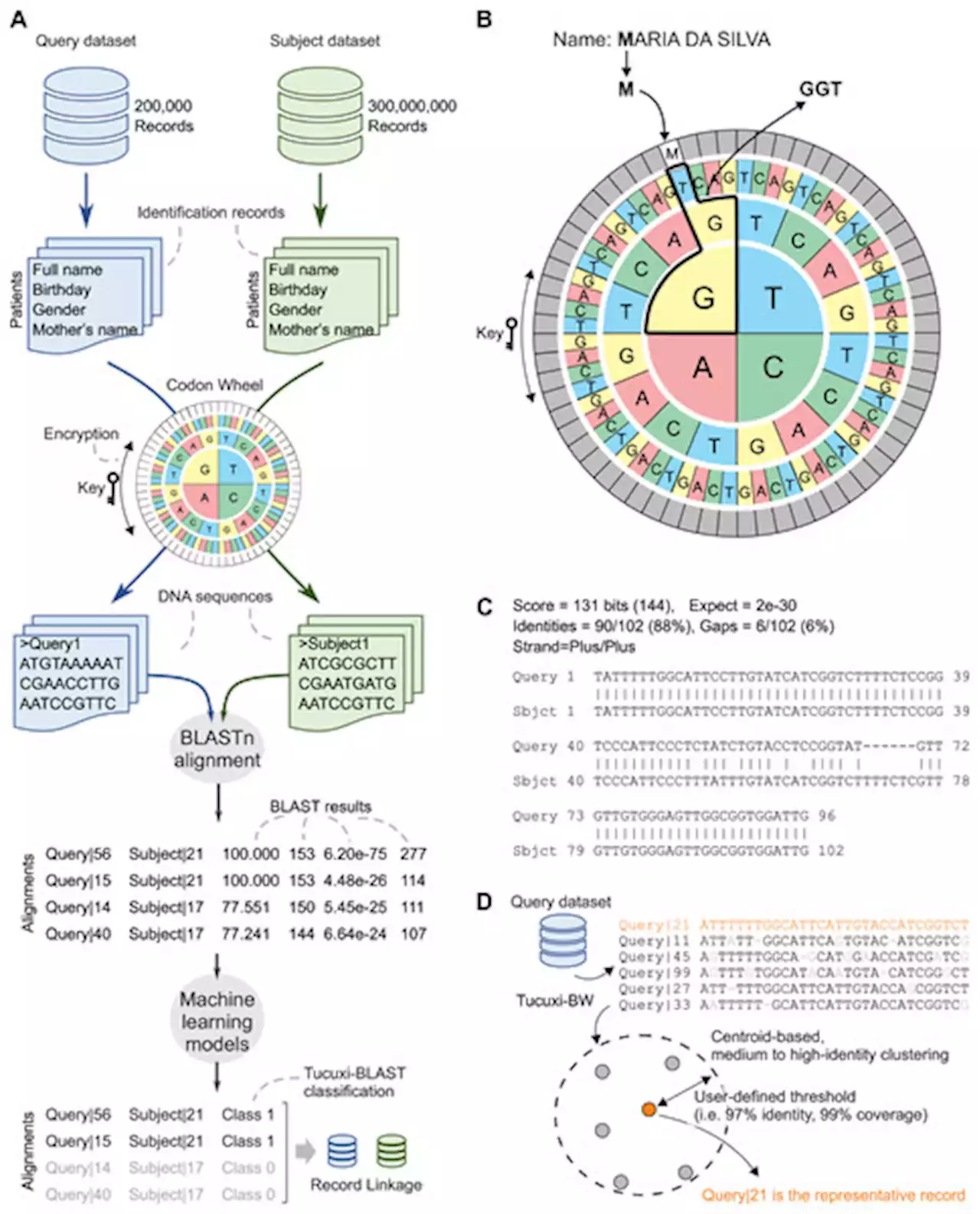 Tucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approachBackground Public health research frequently requires the integration of information from different data sources. However, errors in the records and the high computational costs involved make linking large administrative databases using record linkage (RL) methodologies a major challenge. Methods We present Tucuxi-BLAST, a versatile tool for probabilistic RL that utilizes a DNA-encoded approach to encrypt, analyze and link massive administrative databases. Tucuxi-BLAST encodes the identification records into DNA. BLASTn algorithm is then used to align the sequences between databases. We tested and benchmarked on a simulated database containing records for 300 million individuals and also on four large administrative databases containing real data on Brazilian patients. Results Our method was able to overcome misspellings and typographical errors in administrative databases. In processing the RL of the largest simulated dataset (200k records), the state-of-the-art method took 5 days and 7 h to perform the RL, while Tucuxi-BLAST only took 23 h. When compared with five existing RL tools applied to a gold-standard dataset from real health-related databases, Tucuxi-BLAST had the highest accuracy and speed. By repurposing genomic tools, Tucuxi-BLAST can improve data-driven medical research and provide a fast and accurate way to link individual information across several administrative databases.
Tucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approachBackground Public health research frequently requires the integration of information from different data sources. However, errors in the records and the high computational costs involved make linking large administrative databases using record linkage (RL) methodologies a major challenge. Methods We present Tucuxi-BLAST, a versatile tool for probabilistic RL that utilizes a DNA-encoded approach to encrypt, analyze and link massive administrative databases. Tucuxi-BLAST encodes the identification records into DNA. BLASTn algorithm is then used to align the sequences between databases. We tested and benchmarked on a simulated database containing records for 300 million individuals and also on four large administrative databases containing real data on Brazilian patients. Results Our method was able to overcome misspellings and typographical errors in administrative databases. In processing the RL of the largest simulated dataset (200k records), the state-of-the-art method took 5 days and 7 h to perform the RL, while Tucuxi-BLAST only took 23 h. When compared with five existing RL tools applied to a gold-standard dataset from real health-related databases, Tucuxi-BLAST had the highest accuracy and speed. By repurposing genomic tools, Tucuxi-BLAST can improve data-driven medical research and provide a fast and accurate way to link individual information across several administrative databases.
Read more »
 Kate Garraway left stunned after learning she's related to legendary authorKATE GARRAWAY got more than she bargained for on ITV’s DNA Journey. The Good Morning Britain host, who appears alongside Alison Hammond in tomorrow night’s episode, found she has family links to tw…
Kate Garraway left stunned after learning she's related to legendary authorKATE GARRAWAY got more than she bargained for on ITV’s DNA Journey. The Good Morning Britain host, who appears alongside Alison Hammond in tomorrow night’s episode, found she has family links to tw…
Read more »
