Researchers have developed a new method of measuring qubits, the smallest units of information in a quantum computer, which promises ease of scalability in a microscopic package.
Researchers have developed a new method of measuring qubits, the smallest units of information in a quantum computer , which promises ease of scalability in a microscopic package . Currently, scalability is one of the biggest challenges in developing powerful quantum computer s. An interdisciplinary team of chemists and physicists has outlined a way to teach an AI to make adjustments to the quantum dots that could form the qubits in a quantum computer 's processor.
This new method could potentially revolutionize the field of quantum computing
Qubits Quantum Computer Scalability Microscopic Package Interdisciplinary Team Chemists Physicists AI Quantum Dots Processor Revolutionize Quantum Computing
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 New method enables synthesis of hundreds of new 2D materialsMaterials that are incredibly thin, only a few atoms thick, exhibit unique properties that make them appealing for energy storage, catalysis and water purification. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have now developed a method that enables the synthesis of hundreds of new 2D materials.
New method enables synthesis of hundreds of new 2D materialsMaterials that are incredibly thin, only a few atoms thick, exhibit unique properties that make them appealing for energy storage, catalysis and water purification. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have now developed a method that enables the synthesis of hundreds of new 2D materials.
Read more »
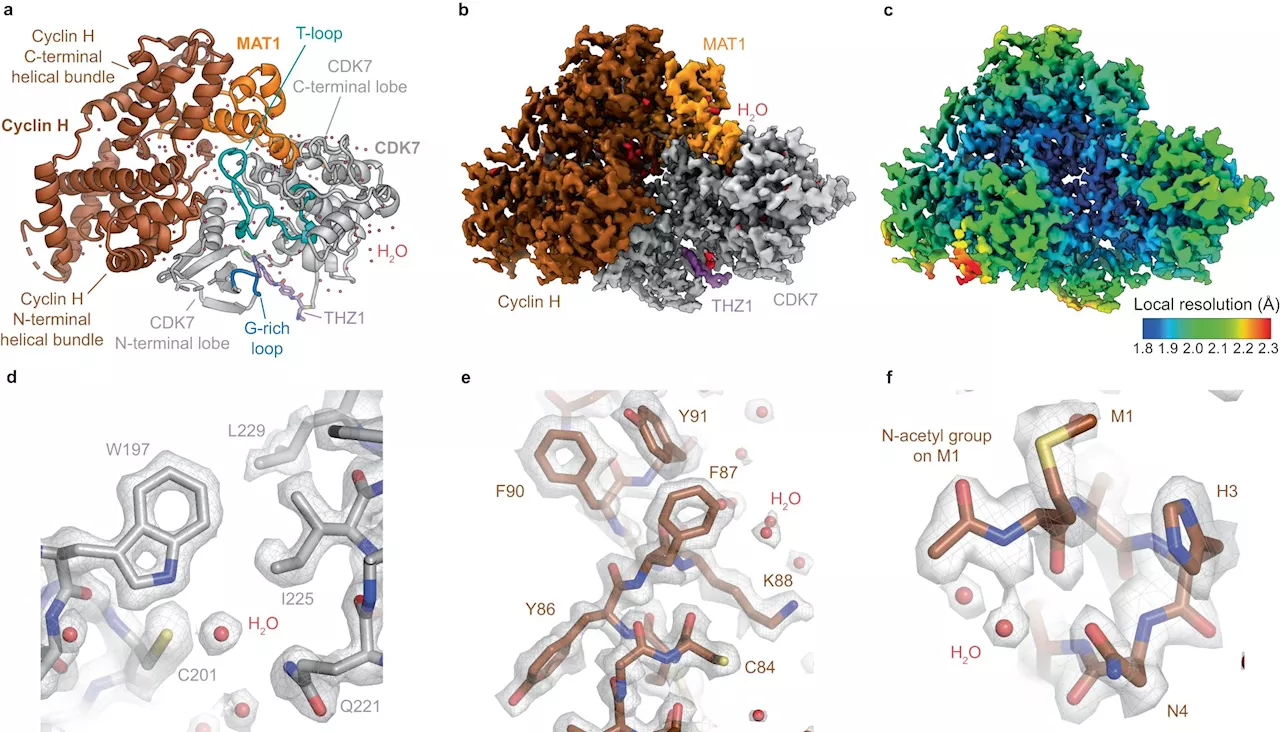 New protein imaging method supports the design of innovative new cancer drugsScientists have successfully used a new imaging technique to determine the structure and interactions of a protein complex that plays a significant part in the initiation and progression of cancer.
New protein imaging method supports the design of innovative new cancer drugsScientists have successfully used a new imaging technique to determine the structure and interactions of a protein complex that plays a significant part in the initiation and progression of cancer.
Read more »
 New Method for Efficient Hydrogen Production Developed in SwedenResearchers in Sweden have developed a new method for efficient hydrogen production that eliminates explosion risks and the need for rare Earth metals. The method separates oxygen and hydrogen generation with a 99 percent efficiency rate, promising easier integration with renewable energies and significant commercial potential.
New Method for Efficient Hydrogen Production Developed in SwedenResearchers in Sweden have developed a new method for efficient hydrogen production that eliminates explosion risks and the need for rare Earth metals. The method separates oxygen and hydrogen generation with a 99 percent efficiency rate, promising easier integration with renewable energies and significant commercial potential.
Read more »
 New method finds higher carnivorous dinosaur biodiversity in Kem Kem beds of MoroccoAn international team of paleontologists from The Netherlands, the UK, Argentina, Germany and Belgium applied recently developed methods to measure theropod (carnivorous) dinosaur species diversity. The newly applied method uses both traditional phylogenetic analysis, discriminant analysis as well as machine learning.
New method finds higher carnivorous dinosaur biodiversity in Kem Kem beds of MoroccoAn international team of paleontologists from The Netherlands, the UK, Argentina, Germany and Belgium applied recently developed methods to measure theropod (carnivorous) dinosaur species diversity. The newly applied method uses both traditional phylogenetic analysis, discriminant analysis as well as machine learning.
Read more »
 New 3D printing method delivers stronger objects, 5 times fasterA novel printing method crafts robust non-metallic materials in record time, 5 times quicker than traditional 3D printing.
New 3D printing method delivers stronger objects, 5 times fasterA novel printing method crafts robust non-metallic materials in record time, 5 times quicker than traditional 3D printing.
Read more »
 A new method for expanding in situ root datasets using CycleGANThe root system is crucial for plants to absorb water and nutrients, with in situ root research providing insights into root phenotypes and dynamics.
A new method for expanding in situ root datasets using CycleGANThe root system is crucial for plants to absorb water and nutrients, with in situ root research providing insights into root phenotypes and dynamics.
Read more »
