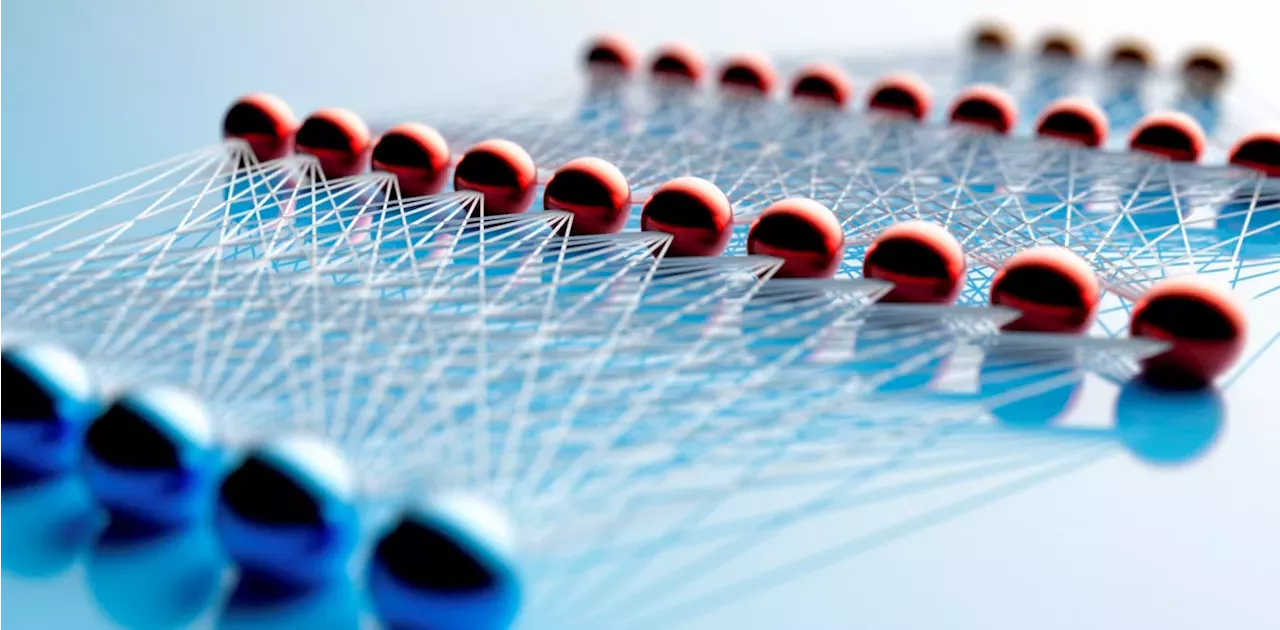
The Nobel Prize shows that the field of artificial neural networks – and the deep learning AI revolution the technology unleashed – owe as much to physics as biology and computer science.
If your jaw dropped as you watched the latest AI-generated video, your bank balance was saved from criminals by a fraud detection system, or your day was made a little easier because you were able to dictate a text message on the run, you have many scientists, mathematicians and engineers to thank.
How a neuron computes Artificial neural networks owe their origins to studies of biological neurons in living brains. In 1943, neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and logician Walter Pitts proposed a simple model of how a neuron works. In the McCulloch-Pitts model, a neuron is connected to its neighboring neurons and can receive signals from them. It can then combine those signals to send signals to other neurons.
Once you’ve made your own decision about whether the new phone is a good choice, other friends can ask you for your recommendation. Similarly, in artificial and biological neural networks, neurons can aggregate signals from their neighbors and send a signal to other neurons.
Hopfield network The initial inspiration for artificial neural networks came from biology, but soon other fields started to shape their development. These included logic, mathematics and physics. The physicist John Hopfield used ideas from physics to study a particular type of recurrent neural network, now called the Hopfield network.
Boltzmann machines and backpropagation During the 1980s, Geoffrey Hinton, computational neurobiologist Terrence Sejnowski and others extended Hopfield’s ideas to create a new class of models called Boltzmann machines, named for the 19th-century physicist Ludwig Boltzmann. As the name implies, the design of these models is rooted in the statistical physics pioneered by Boltzmann.
Artificial Neural Networks Machine Learning Neural Networks Nobel Prize Technology
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 US duo Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun win Nobel Prize in Medicine for 'groundbreaking discovery'The winners for Medicine are selected by the Nobel Assembly of Sweden's Karolinska Institute medical university and receive a prize sum of $1.6 million.
US duo Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun win Nobel Prize in Medicine for 'groundbreaking discovery'The winners for Medicine are selected by the Nobel Assembly of Sweden's Karolinska Institute medical university and receive a prize sum of $1.6 million.
Read more »
 Nobel prize in medicine awarded to scientists for work on microRNAPrize given to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their discovery of microRNA and its role in post-transcriptional gene regulation
Nobel prize in medicine awarded to scientists for work on microRNAPrize given to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their discovery of microRNA and its role in post-transcriptional gene regulation
Read more »
 Nobel Prize in medicine honours American duo for their discovery of microRNAThe Nobel Assembly said that their discovery is "proving to be fundamentally important for how organisms develop and function".
Nobel Prize in medicine honours American duo for their discovery of microRNAThe Nobel Assembly said that their discovery is "proving to be fundamentally important for how organisms develop and function".
Read more »
 Nobel prize in medicine awarded for discovery of microRNAs, the molecules that control our genesUS scientists Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun changed our understanding of how the body works and opened up a new area of science.
Nobel prize in medicine awarded for discovery of microRNAs, the molecules that control our genesUS scientists Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun changed our understanding of how the body works and opened up a new area of science.
Read more »
 Ig Nobel prize goes to team who found mammals can breathe through anusesScientific research on pigeon missiles and dead trout also win at awards for amusing studies with serious implications
Ig Nobel prize goes to team who found mammals can breathe through anusesScientific research on pigeon missiles and dead trout also win at awards for amusing studies with serious implications
Read more »
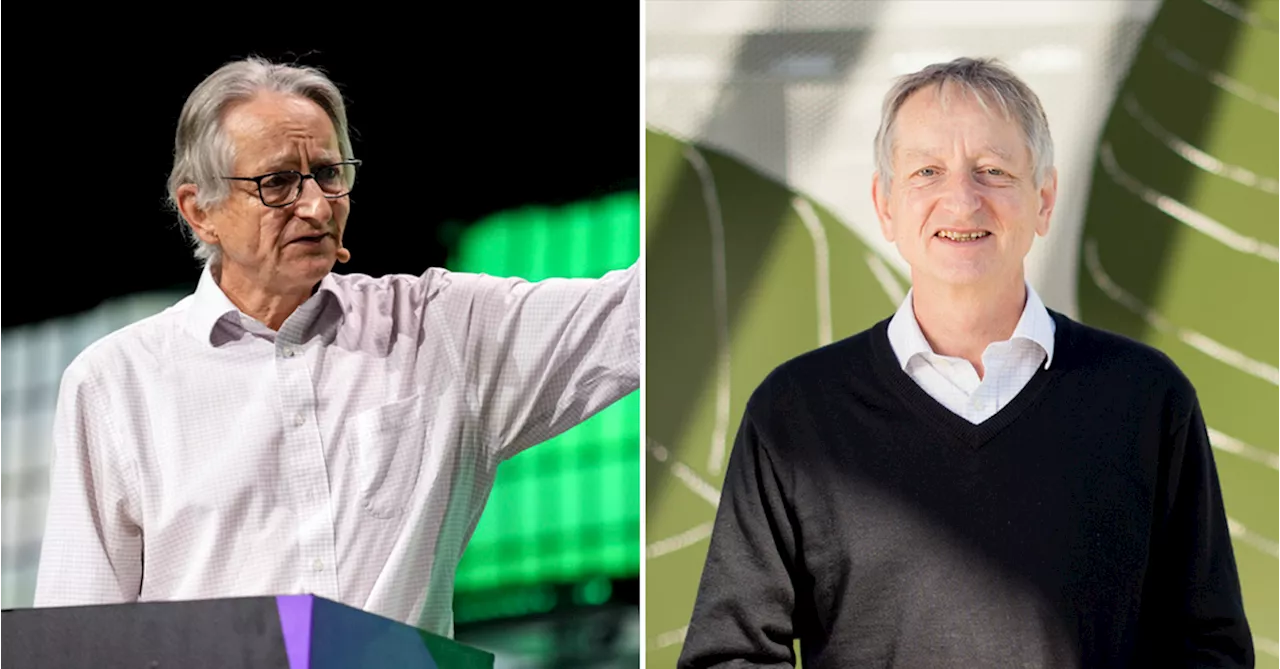 Nobel Prize in physics awarded to two scientists for discoveries that enable machine learningTheir discoveries and inventions formed the building blocks of machine learning, sparking an AI revolution.
Nobel Prize in physics awarded to two scientists for discoveries that enable machine learningTheir discoveries and inventions formed the building blocks of machine learning, sparking an AI revolution.
Read more »