Astronomers captured 'a stunning sequence of images' using NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory spacecraft.
The researchers used a SOHO instrument called the Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph Experiment for the latest approach. This instrument provides long exposures and features a number of color filters that they utilize to gain an enhanced view of the comet's debris trail.
The LASCO instrument's orange filter picks up a narrow range of wavelengths. It is sensitive to sodium, which is typically emitted by near-sun comets when materials sublimate — meaning they are heated so rapidly they are converted from a solid or ice form directly into a gas.
Now that the researchers have an impressive sequence of images in their possession, they will continue to analyze 96P Machholz to learn more about its twin tails ahead of its following approach in June 2028.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Jupiter now has the most moons in the solar systemThis new discovery brings the total number of confirmed moons around Jupiter to 92.
Jupiter now has the most moons in the solar systemThis new discovery brings the total number of confirmed moons around Jupiter to 92.
Read more »
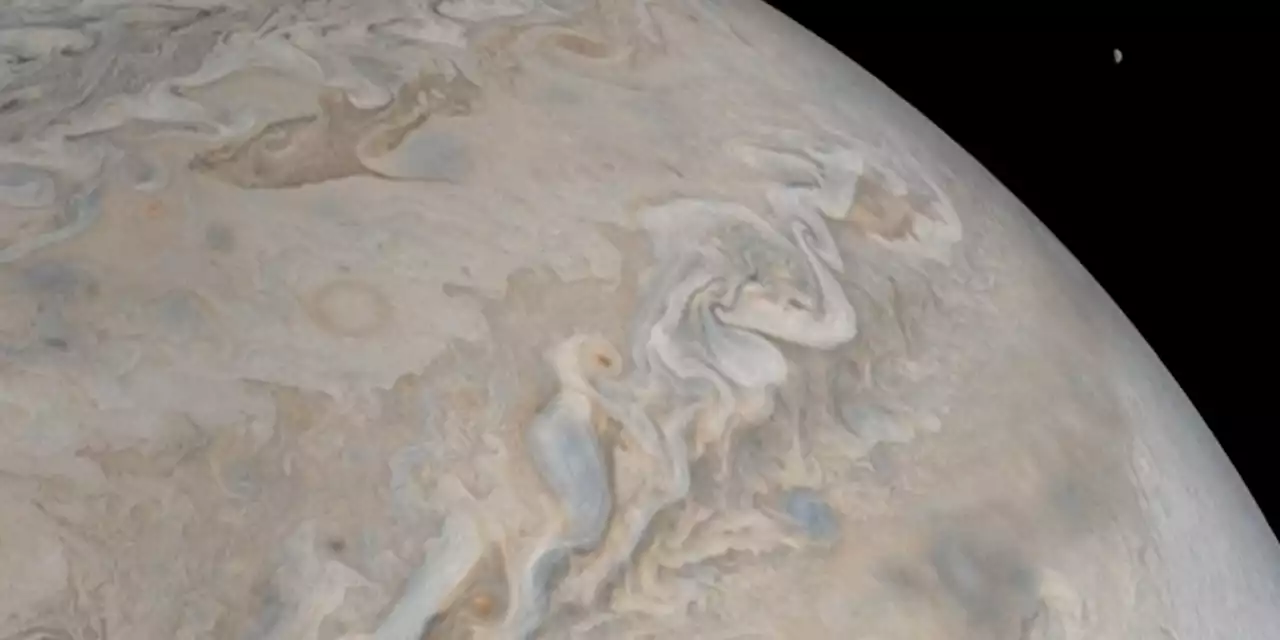 Jupiter now has the most moons in the solar systemAstronomers say they've determined Jupiter has the most moons in solar system.
Jupiter now has the most moons in the solar systemAstronomers say they've determined Jupiter has the most moons in solar system.
Read more »
 Whoa: Astronomers Find New Ring System in the Outer Solar SystemQuaoar, a dwarf planet, has a ring system twice as far out as previously thought possible.
Whoa: Astronomers Find New Ring System in the Outer Solar SystemQuaoar, a dwarf planet, has a ring system twice as far out as previously thought possible.
Read more »
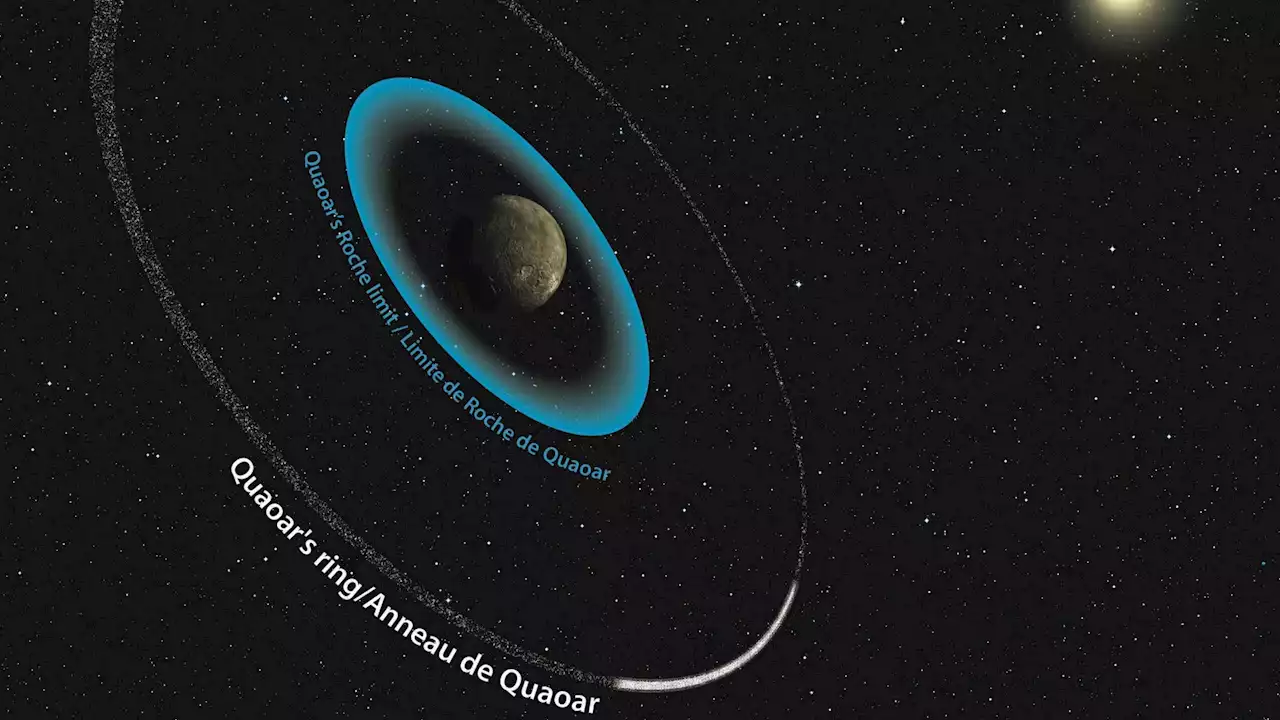 Astronomers discovered breakthrough ring system in our Solar SystemAstronomers have discovered a new ring system around a dwarf planet on the edge of the Solar System that calls into question current theories of how ring systems are formed.
Astronomers discovered breakthrough ring system in our Solar SystemAstronomers have discovered a new ring system around a dwarf planet on the edge of the Solar System that calls into question current theories of how ring systems are formed.
Read more »
 Space Oddities: NASA Sorts Fact From Fantasy | Multimedia Section – NASA Mars Exploration
Space Oddities: NASA Sorts Fact From Fantasy | Multimedia Section – NASA Mars Exploration
Read more »
 A dwarf planet beyond Neptune has a mysterious ring that astronomers can't explainThe ring is so far from the dwarf planet's surface that its material should have coalesced into a moon. But somehow, it didn't.
A dwarf planet beyond Neptune has a mysterious ring that astronomers can't explainThe ring is so far from the dwarf planet's surface that its material should have coalesced into a moon. But somehow, it didn't.
Read more »
