AI predicts cancer patientsurvival by reading doctor's notes ubcnews jamanetworkopen
This attribution method allows us to visualize what words in a document positively or negatively contribute to a prediction. While interpretable, the visualization is specific to words in an individual document; a word’s or phrase’s shown importance may be different in the context of a different document. To protect privacy, we anonymized the shown text by changing dates, names, and other identifying components, ensuring this did not change the interpretation.
has a lower performance across most metrics.compares the performance for our BoW model with one of our best neural models, CNN, when predicting the different survival lengths. On a holdout test set, BoW performed best for predicting 6-month survival, achieving a BAC of 0.856 ; CNN had best performance for predicting 36-month survival, with a BAC of 0.842 and for 60-month survival, with a BAC of 0.837 . We see similar performance between both models.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Efficacy of first dose of covid-19 vaccine versus no vaccination on symptoms of patients with long covid: target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohortObjective To evaluate the effect of covid-19 vaccination on the severity of symptoms in patients with long covid. Design Target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohort. Data source ComPaRe long covid cohort, a nationwide e-cohort (ie, a cohort where recruitment and follow-up are performed online) of patients with long covid, in France. Methods Adult patients (aged ≥18 years) enrolled in the ComPaRe cohort before 1 May 2021 were included in the study if they reported a confirmed or suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection, symptoms persistent for |3 weeks after onset, and at least one symptom attributable to long covid at baseline. Patients who received a first covid-19 vaccine injection were matched with an unvaccinated control group in a 1:1 ratio according to their propensity scores. Number of long covid symptoms, rate of complete remission of long covid, and proportion of patients reporting an unacceptable symptom state at 120 days were recorded. Results 910 patients were included in the analyses (455 in the vaccinated group and 455 in the control group). By 120 days, vaccination had reduced the number of long covid symptoms (mean 13.0 (standard deviation 9.4) in the vaccinated group v 14.8 (9.8) in the control group; mean difference −1.8, 95% confidence interval −3.0 to −0.5) and doubled the rate of patients in remission (16.6% v 7.5%, hazard ratio 1.93, 95% confidence interval 1.18 to 3.14). Vaccination reduced the effect of long covid on patients' lives (mean score on the impact tool 24.3 (standard deviation 16.7) v 27.6 (16.7); mean difference −3.3, 95% confidence interval −5.7 to −1.0) and the proportion of patients with an unacceptable symptom state (38.9% v 46.4%, risk difference −7.4%, 95% confidence interval −14.5% to −0.3%). In the vaccinated group, two (0.4%) patients reported serious adverse events requiring admission to hospital. Conclusion In this study, covid-19 vaccination reduced the severity of symptoms and the effect of long covid on patients' social,
Efficacy of first dose of covid-19 vaccine versus no vaccination on symptoms of patients with long covid: target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohortObjective To evaluate the effect of covid-19 vaccination on the severity of symptoms in patients with long covid. Design Target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohort. Data source ComPaRe long covid cohort, a nationwide e-cohort (ie, a cohort where recruitment and follow-up are performed online) of patients with long covid, in France. Methods Adult patients (aged ≥18 years) enrolled in the ComPaRe cohort before 1 May 2021 were included in the study if they reported a confirmed or suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection, symptoms persistent for |3 weeks after onset, and at least one symptom attributable to long covid at baseline. Patients who received a first covid-19 vaccine injection were matched with an unvaccinated control group in a 1:1 ratio according to their propensity scores. Number of long covid symptoms, rate of complete remission of long covid, and proportion of patients reporting an unacceptable symptom state at 120 days were recorded. Results 910 patients were included in the analyses (455 in the vaccinated group and 455 in the control group). By 120 days, vaccination had reduced the number of long covid symptoms (mean 13.0 (standard deviation 9.4) in the vaccinated group v 14.8 (9.8) in the control group; mean difference −1.8, 95% confidence interval −3.0 to −0.5) and doubled the rate of patients in remission (16.6% v 7.5%, hazard ratio 1.93, 95% confidence interval 1.18 to 3.14). Vaccination reduced the effect of long covid on patients' lives (mean score on the impact tool 24.3 (standard deviation 16.7) v 27.6 (16.7); mean difference −3.3, 95% confidence interval −5.7 to −1.0) and the proportion of patients with an unacceptable symptom state (38.9% v 46.4%, risk difference −7.4%, 95% confidence interval −14.5% to −0.3%). In the vaccinated group, two (0.4%) patients reported serious adverse events requiring admission to hospital. Conclusion In this study, covid-19 vaccination reduced the severity of symptoms and the effect of long covid on patients' social,
Read more »
 Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma: MRI features and their association with survival - Cancer ImagingObjective To evaluate MRI features of sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and their association with survival. Methods This retrospective single-center study included 59 patients with sarcomatoid RCC who underwent MRI before nephrectomy during July 2003–December 2019. Three radiologists reviewed MRI findings of tumor size, non-enhancing areas, lymphadenopathy, and volume (and percentage) of T2 low signal intensity areas (T2LIA). Clinicopathological factors of age, gender, ethnicity, baseline metastatic status, pathological details (subtype and extent of sarcomatoid differentiation), treatment type, and follow-up were extracted. Survival was estimated using Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional-hazards regression model was used to identify factors associated with survival. Results Forty-one males and eighteen females (median age 62 years; interquartile range 51–68) were included. T2LIAs were present in 43 (72.9%) patients. At univariate analysis, clinicopathological factors associated with shorter survival were: greater tumor size (| 10 cm; HR [hazard ratio] = 2.44, 95% CI 1.15–5.21; p = 0.02), metastatic lymph nodes (present; HR = 2.10, 95% CI 1.01–4.37; p = 0.04), extent of sarcomatoid differentiation (non-focal; HR = 3.30, 95% CI 1.55–7.01; p 3.2 mL, HR = 4.22, 95% CI 1.92–9.29); p | 0.01). At multivariate analysis, metastatic disease (HR = 6.89, 95% CI 2.79–16.97; p | 0.01), other subtypes (HR = 9.50, 95% CI 2.81–32.13; p | 0.01), and greater volume of T2LIA (HR = 2.51, 95% CI 1.04–6.05; p = 0.04) remained independently associated with worse survival. Conclusion T2LIAs were present in approximately two thirds of sarcomatoid RCCs. Volume of T2LIA along with clinicopathological factors were associated with survival.
Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma: MRI features and their association with survival - Cancer ImagingObjective To evaluate MRI features of sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and their association with survival. Methods This retrospective single-center study included 59 patients with sarcomatoid RCC who underwent MRI before nephrectomy during July 2003–December 2019. Three radiologists reviewed MRI findings of tumor size, non-enhancing areas, lymphadenopathy, and volume (and percentage) of T2 low signal intensity areas (T2LIA). Clinicopathological factors of age, gender, ethnicity, baseline metastatic status, pathological details (subtype and extent of sarcomatoid differentiation), treatment type, and follow-up were extracted. Survival was estimated using Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional-hazards regression model was used to identify factors associated with survival. Results Forty-one males and eighteen females (median age 62 years; interquartile range 51–68) were included. T2LIAs were present in 43 (72.9%) patients. At univariate analysis, clinicopathological factors associated with shorter survival were: greater tumor size (| 10 cm; HR [hazard ratio] = 2.44, 95% CI 1.15–5.21; p = 0.02), metastatic lymph nodes (present; HR = 2.10, 95% CI 1.01–4.37; p = 0.04), extent of sarcomatoid differentiation (non-focal; HR = 3.30, 95% CI 1.55–7.01; p 3.2 mL, HR = 4.22, 95% CI 1.92–9.29); p | 0.01). At multivariate analysis, metastatic disease (HR = 6.89, 95% CI 2.79–16.97; p | 0.01), other subtypes (HR = 9.50, 95% CI 2.81–32.13; p | 0.01), and greater volume of T2LIA (HR = 2.51, 95% CI 1.04–6.05; p = 0.04) remained independently associated with worse survival. Conclusion T2LIAs were present in approximately two thirds of sarcomatoid RCCs. Volume of T2LIA along with clinicopathological factors were associated with survival.
Read more »
 Relationship between red cell distribution width/albumin ratio and carotid plaque in different glucose metabolic states in patients with coronary heart disease: a RCSCD-TCM study in China - Cardiovascular DiabetologyBackground Red cell distribution width/albumin ratio (RAR) is thought to be associated with the prognosis of a variety of diseases, including diabetes and heart failure. To date, no studies have focused on the relationship between RAR and carotid plaque in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD). Methods A total of 10,267 patients with CHD were divided according to RAR quartiles (Q1: RAR ≤ 2.960; Q2: 2.960 | RAR ≤ 3.185; Q3: 3.185 | RAR | 3.441; Q4: RAR ≥ 3.441). Logistic regression was used to analyze the relationship between RAR and carotid plaques in CHD patients. The relationship between RAR and carotid plaques in according to sex, age and glucose regulation state groups were also assessed. Results Among the 10,267 participants, 75.43% had carotid plaques. After adjusting for confounding factors, RAR was found to be associated with carotid plaque formation (OR: 1.23; 95% CI 1.08–1.39). The risk of carotid plaque formation in the Q4 group was 1.24 times higher than that in the Q1 group. After multivariate adjustment, RAR was associated with the risk of carotid plaque in female (OR: 1.29; 95% CI 1.09–1.52). And the relationship between RAR and carotid plaques in patients younger than 60 years old (OR: 1.43; 95% CI 1.16–1.75) was stronger than that in those older than 60 years old (OR: 1.29; 95% CI 1.10–1.51). Under different glucose metabolism states, RAR had the highest correlation with the risk of carotid plaques in diabetes patients (OR: 1.28; 95% CI 1.04–1.58). Conclusions RAR was significantly related to carotid plaques in patients with CHD. In addition, the correlation between RAR and the incidence of carotid plaque in patients with CHD was higher in women and middle-aged and elderly patients. In patients with CHD and diabetes, the correlation between RAR and carotid plaque was higher. Graphical Abstract
Relationship between red cell distribution width/albumin ratio and carotid plaque in different glucose metabolic states in patients with coronary heart disease: a RCSCD-TCM study in China - Cardiovascular DiabetologyBackground Red cell distribution width/albumin ratio (RAR) is thought to be associated with the prognosis of a variety of diseases, including diabetes and heart failure. To date, no studies have focused on the relationship between RAR and carotid plaque in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD). Methods A total of 10,267 patients with CHD were divided according to RAR quartiles (Q1: RAR ≤ 2.960; Q2: 2.960 | RAR ≤ 3.185; Q3: 3.185 | RAR | 3.441; Q4: RAR ≥ 3.441). Logistic regression was used to analyze the relationship between RAR and carotid plaques in CHD patients. The relationship between RAR and carotid plaques in according to sex, age and glucose regulation state groups were also assessed. Results Among the 10,267 participants, 75.43% had carotid plaques. After adjusting for confounding factors, RAR was found to be associated with carotid plaque formation (OR: 1.23; 95% CI 1.08–1.39). The risk of carotid plaque formation in the Q4 group was 1.24 times higher than that in the Q1 group. After multivariate adjustment, RAR was associated with the risk of carotid plaque in female (OR: 1.29; 95% CI 1.09–1.52). And the relationship between RAR and carotid plaques in patients younger than 60 years old (OR: 1.43; 95% CI 1.16–1.75) was stronger than that in those older than 60 years old (OR: 1.29; 95% CI 1.10–1.51). Under different glucose metabolism states, RAR had the highest correlation with the risk of carotid plaques in diabetes patients (OR: 1.28; 95% CI 1.04–1.58). Conclusions RAR was significantly related to carotid plaques in patients with CHD. In addition, the correlation between RAR and the incidence of carotid plaque in patients with CHD was higher in women and middle-aged and elderly patients. In patients with CHD and diabetes, the correlation between RAR and carotid plaque was higher. Graphical Abstract
Read more »
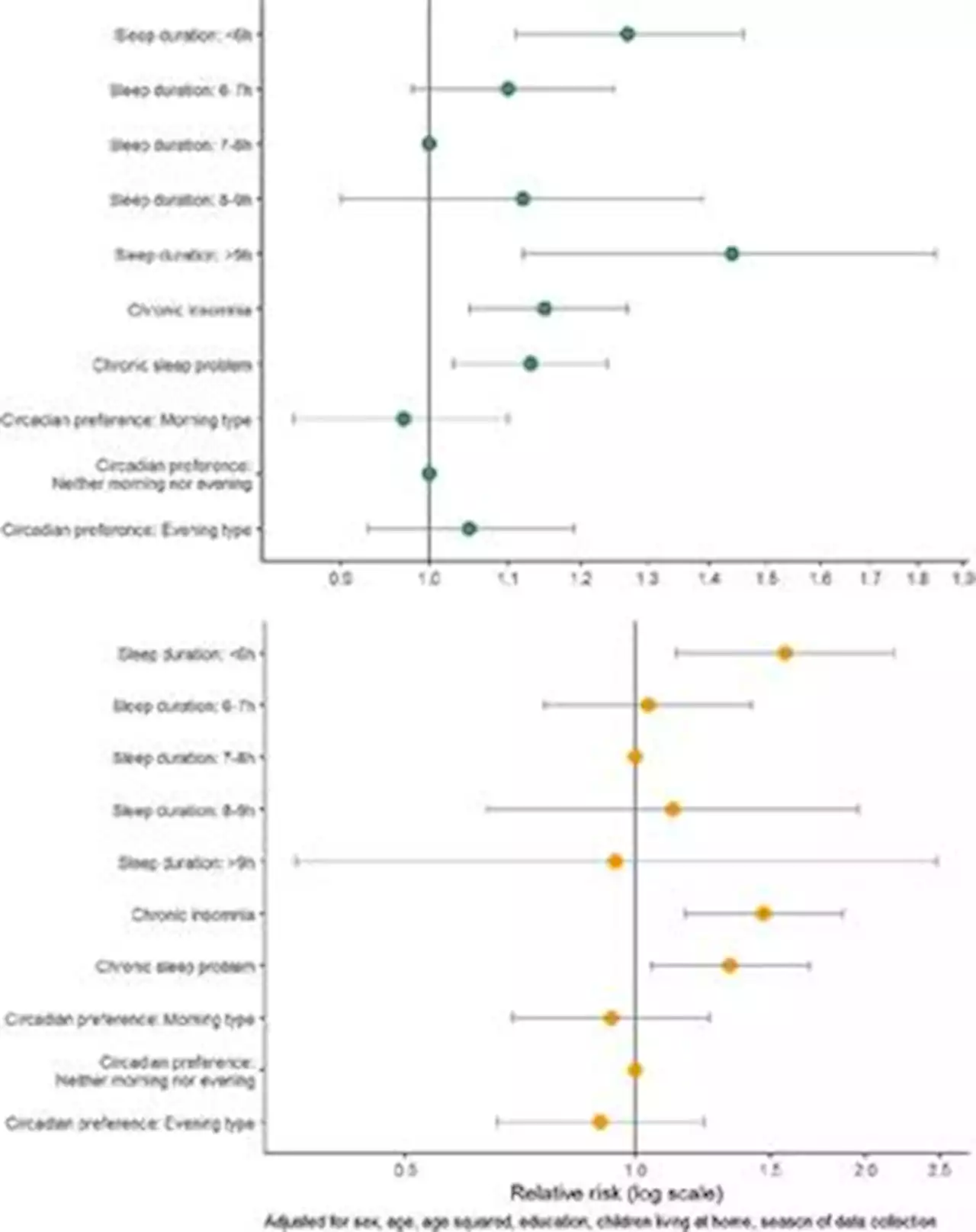 Frontiers | The association between self-reported sleep problems, infection, and antibiotic use in patients in general practiceObjectives: There is emerging evidence that sleep problems and short sleep duration increase the risk of infection. We aimed to assess whether chronic insomnia disorder, chronic sleep problems, sleep duration and circadian preference based on self-report were associated with risk of infections and antibiotic use among patients visiting their general practitioner (GP). Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 1848 unselected patients in Norway visiting their GP during 2020.The patients completed a one-page questionnaire while waiting for the consultation, that included the validated Bergen Insomnia Scale (BIS), questions on self-assessedassessed sleep problem, sleep duration and circadian preference and whether they have had any infections or used antibiotics in the last three months. Relative risks (RR) were estimated using modified Poisson regression models. Results: The risk of infection was 27% (95% CI RR 1.11-1.46) and 44% higher (95% CI 1.12-1.84) in patients sleeping 9 hours, respectively, compared to those sleeping 7-8 hours. The risk was also increased in patients with chronic insomnia disorder or a chronic sleep problem. For antibiotic use, the risk was higher for patients sleeping |6 hours, and for those with chronic insomnia disorder or a chronic sleep problem. Conclusions: Among patients visiting their GP, short sleep duration, chronic insomnia and chronic sleep problem based on self-report were associated with higher prevalence of infection and antibiotic use. These findings support the notion of a strong association between sleep and infection.
Frontiers | The association between self-reported sleep problems, infection, and antibiotic use in patients in general practiceObjectives: There is emerging evidence that sleep problems and short sleep duration increase the risk of infection. We aimed to assess whether chronic insomnia disorder, chronic sleep problems, sleep duration and circadian preference based on self-report were associated with risk of infections and antibiotic use among patients visiting their general practitioner (GP). Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 1848 unselected patients in Norway visiting their GP during 2020.The patients completed a one-page questionnaire while waiting for the consultation, that included the validated Bergen Insomnia Scale (BIS), questions on self-assessedassessed sleep problem, sleep duration and circadian preference and whether they have had any infections or used antibiotics in the last three months. Relative risks (RR) were estimated using modified Poisson regression models. Results: The risk of infection was 27% (95% CI RR 1.11-1.46) and 44% higher (95% CI 1.12-1.84) in patients sleeping 9 hours, respectively, compared to those sleeping 7-8 hours. The risk was also increased in patients with chronic insomnia disorder or a chronic sleep problem. For antibiotic use, the risk was higher for patients sleeping |6 hours, and for those with chronic insomnia disorder or a chronic sleep problem. Conclusions: Among patients visiting their GP, short sleep duration, chronic insomnia and chronic sleep problem based on self-report were associated with higher prevalence of infection and antibiotic use. These findings support the notion of a strong association between sleep and infection.
Read more »
 Sons of the Forest is the funniest videogame on the internet right nowThe survival sim with creepy cannibals is surprisingly joyful.
Sons of the Forest is the funniest videogame on the internet right nowThe survival sim with creepy cannibals is surprisingly joyful.
Read more »
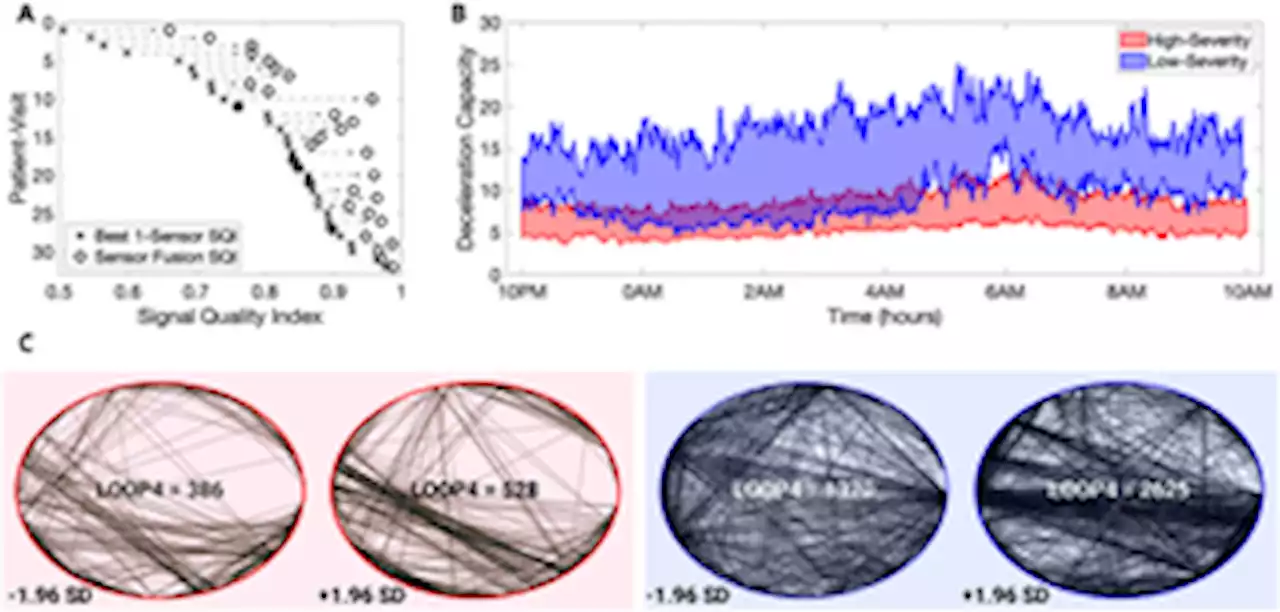 Rett syndrome severity estimation with the BioStamp nPoint using interactions between heart rate variability and body movementRett syndrome, a rare genetic neurodevelopmental disorder in humans, does not have an effective cure. However, multiple therapies and medications exist to treat symptoms and improve patients’ quality of life. As research continues to discover and evaluate new medications for Rett syndrome patients, there remains a lack of objective physiological and motor activity-based (physio-motor) biomarkers that enable the measurement of the effect of these medications on the change in patients’ Rett syndrome severity. In our work, using a commercially available wearable chest patch, we recorded simultaneous electrocardiogram and three-axis acceleration from 20 patients suffering from Rett syndrome along with the corresponding Clinical Global Impression—Severity score, which measures the overall disease severity on a 7-point Likert scale. We derived physio-motor features from these recordings that captured heart rate variability, activity metrics, and the interactions between heart rate and activity. Further, we developed machine learning (ML) models to classify high-severity Rett patients from low-severity Rett patients using the derived physio-motor features. For the best-trained model, we obtained a pooled area under the receiver operating curve equal to 0.92 via a leave-one-out-patient cross-validation approach. Finally, we computed the feature popularity scores for all the trained ML models and identified physio-motor biomarkers for Rett syndrome.
Rett syndrome severity estimation with the BioStamp nPoint using interactions between heart rate variability and body movementRett syndrome, a rare genetic neurodevelopmental disorder in humans, does not have an effective cure. However, multiple therapies and medications exist to treat symptoms and improve patients’ quality of life. As research continues to discover and evaluate new medications for Rett syndrome patients, there remains a lack of objective physiological and motor activity-based (physio-motor) biomarkers that enable the measurement of the effect of these medications on the change in patients’ Rett syndrome severity. In our work, using a commercially available wearable chest patch, we recorded simultaneous electrocardiogram and three-axis acceleration from 20 patients suffering from Rett syndrome along with the corresponding Clinical Global Impression—Severity score, which measures the overall disease severity on a 7-point Likert scale. We derived physio-motor features from these recordings that captured heart rate variability, activity metrics, and the interactions between heart rate and activity. Further, we developed machine learning (ML) models to classify high-severity Rett patients from low-severity Rett patients using the derived physio-motor features. For the best-trained model, we obtained a pooled area under the receiver operating curve equal to 0.92 via a leave-one-out-patient cross-validation approach. Finally, we computed the feature popularity scores for all the trained ML models and identified physio-motor biomarkers for Rett syndrome.
Read more »