Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia worldwide with around 59 million people concerned in 2019. This irregular heartbeat is associated with increased risks of heart failure, dementia and stroke. It constitutes a significant burden to health care systems, making its early detection and treatment a major goal.
Researchers develop deep-learning model capable of predicting cardiac arrhythmia 30 minutes before it happens retrieved 22 April 2024 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-04-deep-capable-cardiac-arrhythmia-minutes.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Medicine Research Health Research News Health Research Health Science Medicine Science
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
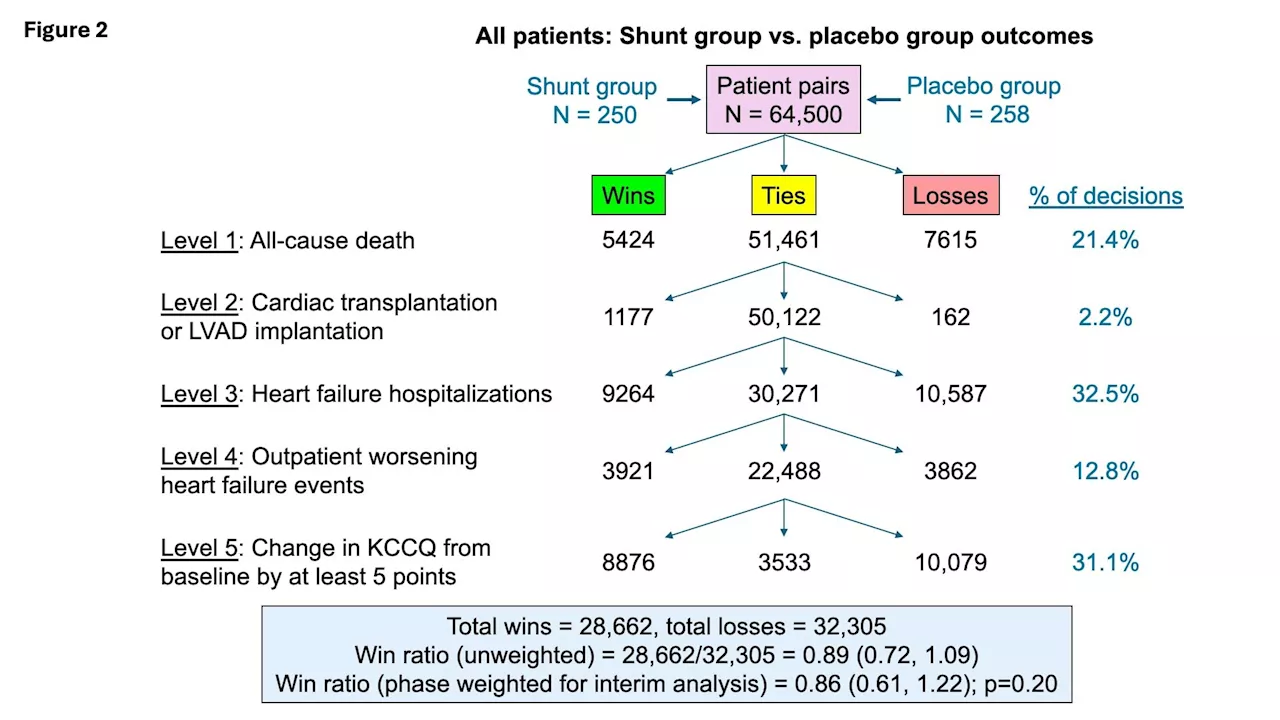 Inter-atrial shunts may benefit some heart failure patients while harming others, trial findsInter-atrial shunts—investigational devices that create a small pathway for blood to pass from the left to the right side of the heart in order to improve heart failure symptoms and outcomes—may be beneficial to heart failure patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) but harmful or even deadly for heart failure patients with...
Inter-atrial shunts may benefit some heart failure patients while harming others, trial findsInter-atrial shunts—investigational devices that create a small pathway for blood to pass from the left to the right side of the heart in order to improve heart failure symptoms and outcomes—may be beneficial to heart failure patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) but harmful or even deadly for heart failure patients with...
Read more »
 Study shows heart failure, not stroke is the most common complication of atrial fibrillationThe lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation (a heart condition that causes an irregular and often abnormally fast heart rate) has increased from one in four to one in three over the past two decades, finds a study from Denmark in The BMJ today.
Study shows heart failure, not stroke is the most common complication of atrial fibrillationThe lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation (a heart condition that causes an irregular and often abnormally fast heart rate) has increased from one in four to one in three over the past two decades, finds a study from Denmark in The BMJ today.
Read more »
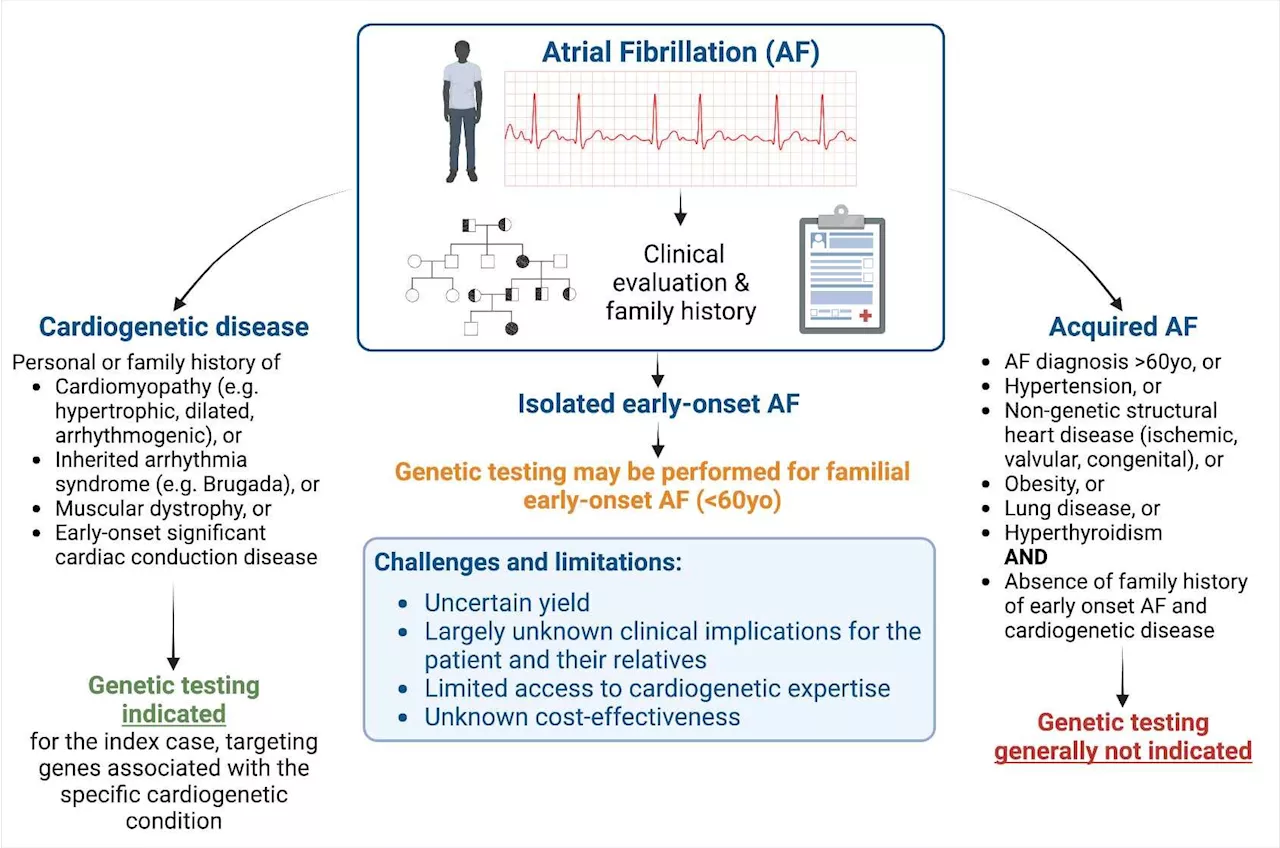 Genetic testing of patients with atrial fibrillation can alert clinicians to potential life-threatening conditionsAlthough the vast majority of clinicians do not view atrial fibrillation (AF) as a genetic disorder, a White Paper in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology analyzes the current understanding of genetics and the role of genetic testing in AF and concludes there is an increasing appreciation that genetic culprits for potentially life-threatening...
Genetic testing of patients with atrial fibrillation can alert clinicians to potential life-threatening conditionsAlthough the vast majority of clinicians do not view atrial fibrillation (AF) as a genetic disorder, a White Paper in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology analyzes the current understanding of genetics and the role of genetic testing in AF and concludes there is an increasing appreciation that genetic culprits for potentially life-threatening...
Read more »
 New research advocates genetic screening in early onset atrial fibrillationAlthough the vast majority of clinicians do not view atrial fibrillation (AF) as a genetic disorder, a White Paper in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, analyzes the current understanding of genetics and the role of genetic testing in AF and concludes there is an increasing appreciation that genetic culprits for potentially...
New research advocates genetic screening in early onset atrial fibrillationAlthough the vast majority of clinicians do not view atrial fibrillation (AF) as a genetic disorder, a White Paper in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, analyzes the current understanding of genetics and the role of genetic testing in AF and concludes there is an increasing appreciation that genetic culprits for potentially...
Read more »
 Patients with device-detected atrial fibrillation and multiple comorbidities do not benefit from anticoagulation: StudyIn patients with device-detected atrial fibrillation and a high comorbidity burden, oral anticoagulation increases bleeding without a clear reduction in stroke. This is the main finding of a sub-analysis of the NOAH–AFNET 6 trial presented by Dr.
Patients with device-detected atrial fibrillation and multiple comorbidities do not benefit from anticoagulation: StudyIn patients with device-detected atrial fibrillation and a high comorbidity burden, oral anticoagulation increases bleeding without a clear reduction in stroke. This is the main finding of a sub-analysis of the NOAH–AFNET 6 trial presented by Dr.
Read more »
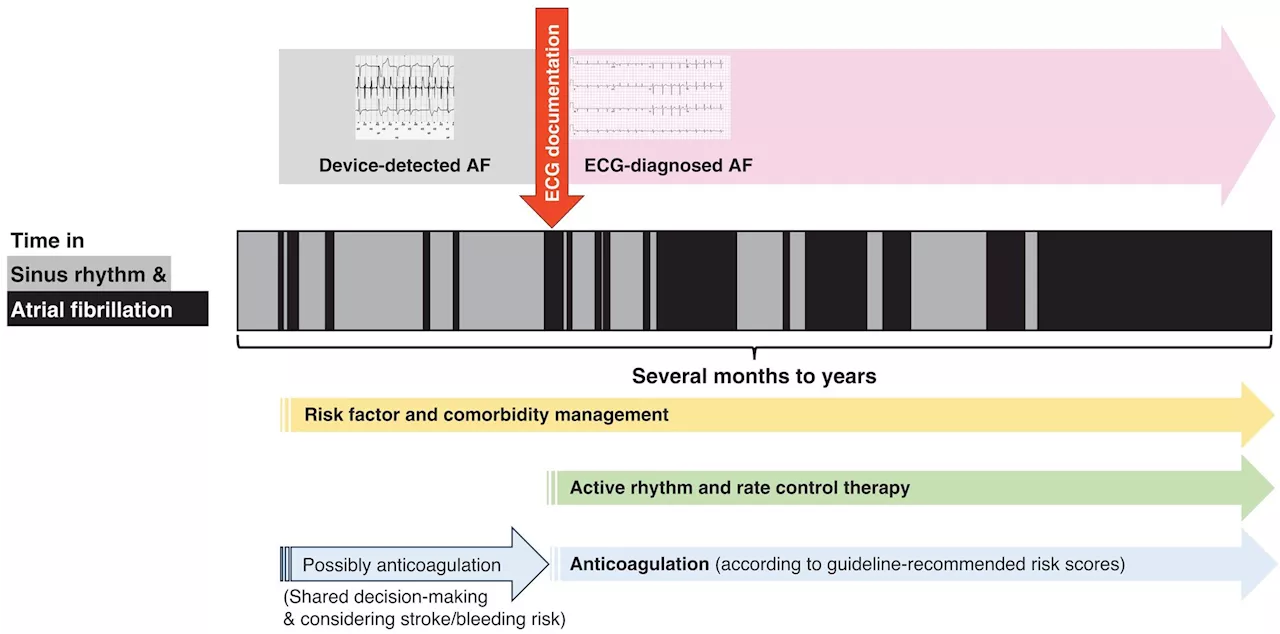 Experts give recommendations for longer and better lives for patients with atrial fibrillationAn international panel of experts published recommendations to improve management of atrial fibrillation (AF).
Experts give recommendations for longer and better lives for patients with atrial fibrillationAn international panel of experts published recommendations to improve management of atrial fibrillation (AF).
Read more »
