SARS-CoV-2 envelope structural protein found to form voltage-activated and calcium-activated calcium channels biorixvpreprint dundeeuni COVID19 SARSCoV2 Envelope Protein CalciumChannel
By Pooja Toshniwal PahariaOct 14 2022Reviewed by Aimee Molineux In a recent study posted to the bioRxiv* preprint server, researchers investigated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 envelope protein activity in terms of calcium cations cations.
About the study In the present study, researchers explored the prime physiological function of SARS-CoV-2 E upon viral infection. In addition, the effects of post-translational modifications on the E protein function were explored by palmitoylating all the cysteine residues in every subunit in the EFL pentamers of SARS-CoV-2 E protein channels. Further, the effects of luminal Ca2+ concentrations on EFL gating properties were evaluated.
The hydrophobically gated ion channel activity of the viral E protein and viroporins were regulated by elevated luminal Ca2+ concentrations , electrochemical gradients, pH, PTMs, ERGIC phospholipids with negative charges, and voltage applied to the membranes. Palmitoylation of ≥1 cysteine residue promoted the formation of open and stable E protein pores. Ca2+ ions activated ER-luminal channels and maintained the pores in the open state.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Study describes the first SARS-CoV-2 Deltacron recombinant case identified in BrazilStudy describes the first SARS-CoV-2 Deltacron recombinant case identified in Brazil biorxivpreprint uniofeastanglia SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid Delta Omicron
Study describes the first SARS-CoV-2 Deltacron recombinant case identified in BrazilStudy describes the first SARS-CoV-2 Deltacron recombinant case identified in Brazil biorxivpreprint uniofeastanglia SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid Delta Omicron
Read more »
 Motif-based SARS-CoV-2 protein-human protein interactions as potential antiviral target sitesResearchers performed a ProP-PD (proteomic peptide phage display) analysis to identify peptides from intrinsically disordered human (host) proteome regions that bind with SARS-CoV-2 genome-encoded folded protein domains (PDs).
Motif-based SARS-CoV-2 protein-human protein interactions as potential antiviral target sitesResearchers performed a ProP-PD (proteomic peptide phage display) analysis to identify peptides from intrinsically disordered human (host) proteome regions that bind with SARS-CoV-2 genome-encoded folded protein domains (PDs).
Read more »
JCI - Improved control of SARS-CoV-2 by treatment with nucleocapsid-specific monoclonal antibody
Read more »
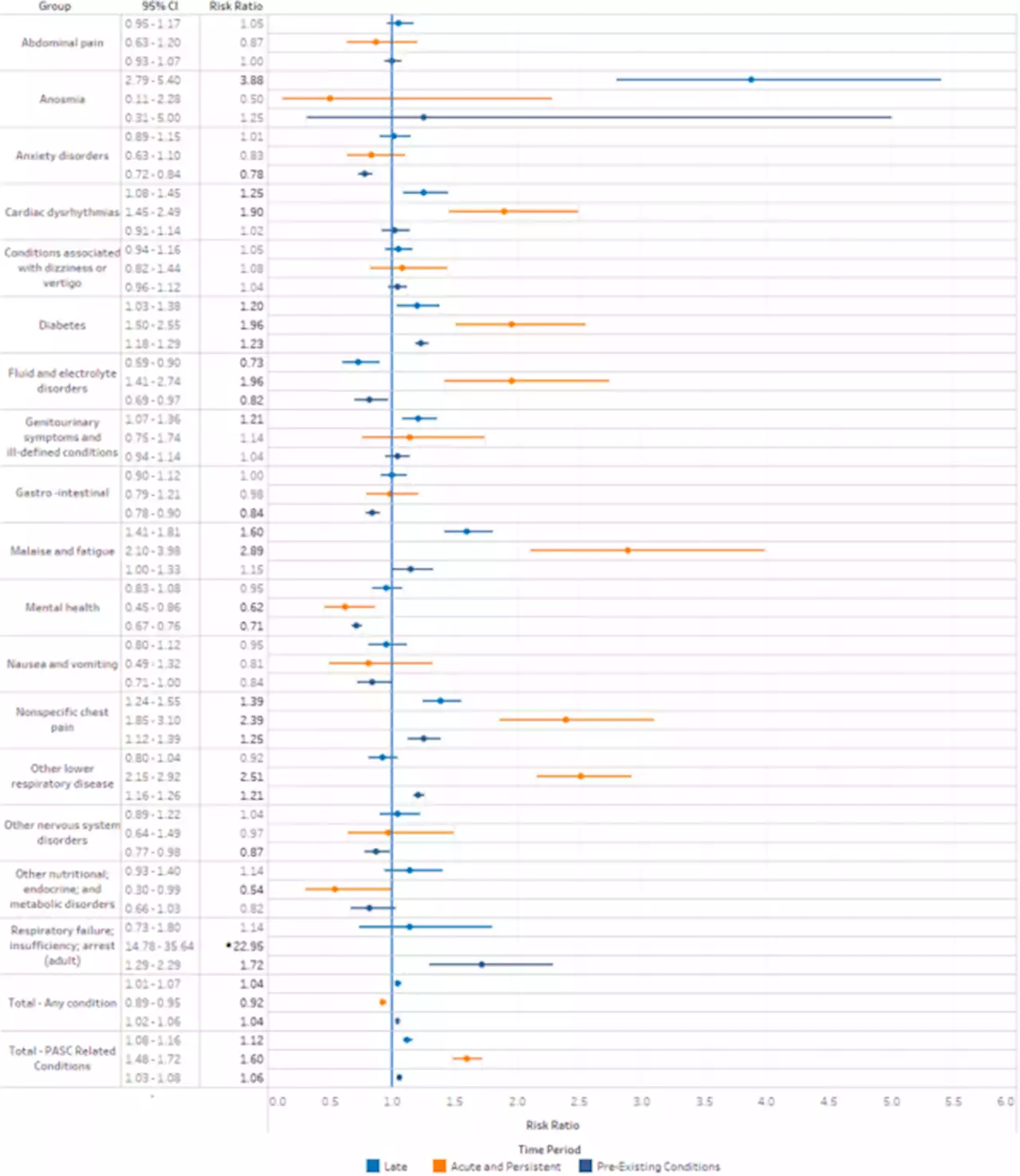 Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 with clinical condition definitions and comparison in a matched cohort - Nature CommunicationsIn this study, the authors use electronic health record data from the US to characterise post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC). They identify 17 common PASC conditions and find an overall ~12% increase in risk of PASC conditions in the post-acute period among people with a SARS-CoV-2 positive test compared to matched test-negative controls.
Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 with clinical condition definitions and comparison in a matched cohort - Nature CommunicationsIn this study, the authors use electronic health record data from the US to characterise post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC). They identify 17 common PASC conditions and find an overall ~12% increase in risk of PASC conditions in the post-acute period among people with a SARS-CoV-2 positive test compared to matched test-negative controls.
Read more »
 Frontiers | Myocarditis in SARS-CoV-2 infection vs. COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysisBackground: To compare the incidence of myocarditis in COVID-19 vaccines and SARS-CoV-2 infection groups. Methods: Electronic databases (MEDLINE, Scopus, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and the World Health Organization Global Literature on Coronavirus Disease) and trial registries were searched to April 2022, for randomized controlled trials and observational cohort studies reporting the risk of myocarditis associated with the COVID-19 vaccines and the risk associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. We estimated the effect of COVID-19 infection and vaccines on rates of myocarditis by random-effects meta-analyses using the generic inverse variance method. Meta-regression analyses were conducted to assess the effect sex and age on the incidence of myocarditis. Results: We identified 22 eligible studies consisting of 55.5 million vaccinated cohort and 2.5 million in the infection cohort. Median age was 49 years (interquartile range (IQR): 38-56), and 49% (IQR: 43% to 52%) were male. Of patients diagnosed with myocarditis, 3.48 (%) were hospitalized and 0.05 (%) died. The relative risk (RR) for myocarditis was 7 times in the infection group than vaccination group (RR: 15 (95% CI: 11.09 - 19.81, infection group) and RR: 2.0 (95% CI: 1.44-2.65, vaccine group). Of patients who developed myocarditis after receiving the vaccine or having the infection, 61 (IQR: 39% -87%) were male. Meta- regression analysis indicated that male sex and young age were associated with myocarditis. A slow decline in the rates of myocarditis was observed as a function of time from vaccination. Risk of bias assessment was moderate. Conclusions: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we found that the risk of incident myocarditis is about 7 times higher in persons who were infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus than those who received the vaccine. These findings support continued use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines among all eligible persons aged ≥5 years
Frontiers | Myocarditis in SARS-CoV-2 infection vs. COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysisBackground: To compare the incidence of myocarditis in COVID-19 vaccines and SARS-CoV-2 infection groups. Methods: Electronic databases (MEDLINE, Scopus, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and the World Health Organization Global Literature on Coronavirus Disease) and trial registries were searched to April 2022, for randomized controlled trials and observational cohort studies reporting the risk of myocarditis associated with the COVID-19 vaccines and the risk associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. We estimated the effect of COVID-19 infection and vaccines on rates of myocarditis by random-effects meta-analyses using the generic inverse variance method. Meta-regression analyses were conducted to assess the effect sex and age on the incidence of myocarditis. Results: We identified 22 eligible studies consisting of 55.5 million vaccinated cohort and 2.5 million in the infection cohort. Median age was 49 years (interquartile range (IQR): 38-56), and 49% (IQR: 43% to 52%) were male. Of patients diagnosed with myocarditis, 3.48 (%) were hospitalized and 0.05 (%) died. The relative risk (RR) for myocarditis was 7 times in the infection group than vaccination group (RR: 15 (95% CI: 11.09 - 19.81, infection group) and RR: 2.0 (95% CI: 1.44-2.65, vaccine group). Of patients who developed myocarditis after receiving the vaccine or having the infection, 61 (IQR: 39% -87%) were male. Meta- regression analysis indicated that male sex and young age were associated with myocarditis. A slow decline in the rates of myocarditis was observed as a function of time from vaccination. Risk of bias assessment was moderate. Conclusions: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we found that the risk of incident myocarditis is about 7 times higher in persons who were infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus than those who received the vaccine. These findings support continued use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines among all eligible persons aged ≥5 years
Read more »
 Emerging investigator series: meta-analyses on SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA levels in wastewater and their correlations to epidemiological indicatorsBackground: recent applications of wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) have demonstrated its ability to track the spread and dynamics of COVID-19 at the community level. Despite the growing body of research, quantitative synthesis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA levels in wastewater generated from studies across
Emerging investigator series: meta-analyses on SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA levels in wastewater and their correlations to epidemiological indicatorsBackground: recent applications of wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) have demonstrated its ability to track the spread and dynamics of COVID-19 at the community level. Despite the growing body of research, quantitative synthesis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA levels in wastewater generated from studies across
Read more »
