Sounds like a premise for a superhero movie!
In news that seems like it just might lead to a strange new superhero, Japanese scientists say cultured human muscle cells can stay swole with an injection of, well, bear serum., is bears' ability to hibernate for extended periods of time without losing muscle mass.
"Hibernating animals are likely better described to be under the 'no use, but no lose' phenomenon, in that there is potential resistance to muscle atrophy during continued disuse conditions," study author Mitsunori Miyazaki said in the press release.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 A mystery ingredient in bears' blood could supercharge human muscle growthHibernating animals like bears can stay asleep for months without showing any signs of muscle loss.
A mystery ingredient in bears' blood could supercharge human muscle growthHibernating animals like bears can stay asleep for months without showing any signs of muscle loss.
Read more »
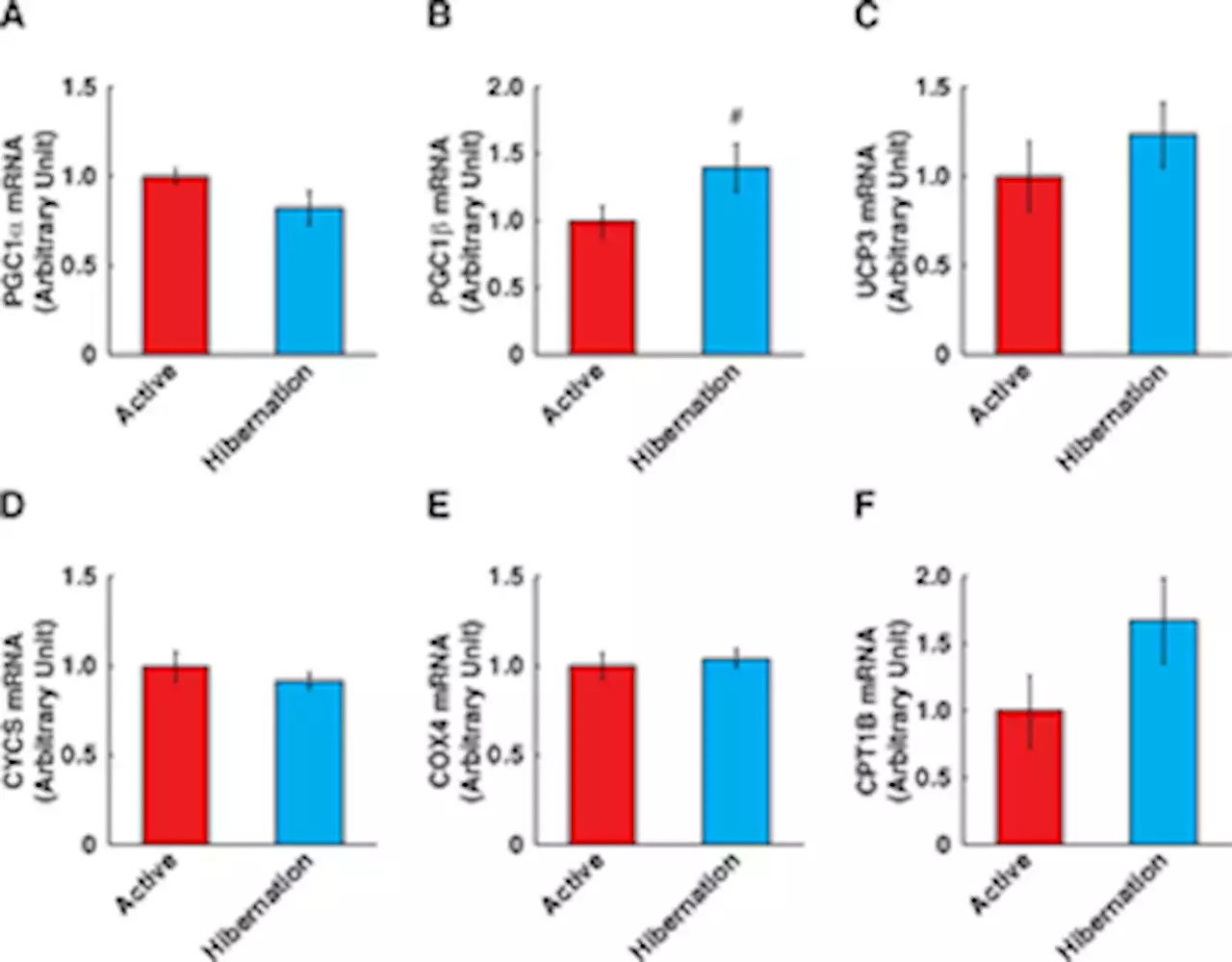 Supplementing cultured human myotubes with hibernating bear serum results in increased protein content by modulating Akt/FOXO3a signalingHibernating bears remain in their dens for 5–7 months during winter and survive without eating or drinking while staying inactive. However, they maintain their physical functions with minimal skeletal muscle atrophy and metabolic dysfunction. In bears, resistance to skeletal muscle atrophy during hibernation is likely mediated by seasonally altered systemic factors that are independent of neuromuscular activity. To determine whether there are components in bear serum that regulate protein and energy metabolism, differentiated human skeletal muscle cells were treated with bear serum (5% in DMEM/Ham’s F-12, 24 h) collected during active summer (July) and hibernating winter (February) periods. The serum samples were collected from the same individual bears (Ursus thibetanus japonicus, n=7 in each season). Total protein content in cultured skeletal muscle cells was significantly increased following a 24 h treatment with hibernating bear serum. Although the protein synthesis rate was not altered, the expression of MuRF1 protein, a muscle-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase was significantly decreased along with a concomitant activation of Akt/FOXO3a signaling. Increased levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) were also observed in hibernating bear serum. These observations suggest that protein metabolism in cultured human myotubes may be altered when incubated with hibernating bear serum, with a significant increase in serum IGF-1 and diminished MuRF1 expression, a potential target of Akt/FOXO3a signaling. A protein sparing phenotype in cultured muscle cells by treatment with hibernating bear serum holds potential for the development of methods to prevent human muscle atrophy and related disorders.
Supplementing cultured human myotubes with hibernating bear serum results in increased protein content by modulating Akt/FOXO3a signalingHibernating bears remain in their dens for 5–7 months during winter and survive without eating or drinking while staying inactive. However, they maintain their physical functions with minimal skeletal muscle atrophy and metabolic dysfunction. In bears, resistance to skeletal muscle atrophy during hibernation is likely mediated by seasonally altered systemic factors that are independent of neuromuscular activity. To determine whether there are components in bear serum that regulate protein and energy metabolism, differentiated human skeletal muscle cells were treated with bear serum (5% in DMEM/Ham’s F-12, 24 h) collected during active summer (July) and hibernating winter (February) periods. The serum samples were collected from the same individual bears (Ursus thibetanus japonicus, n=7 in each season). Total protein content in cultured skeletal muscle cells was significantly increased following a 24 h treatment with hibernating bear serum. Although the protein synthesis rate was not altered, the expression of MuRF1 protein, a muscle-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase was significantly decreased along with a concomitant activation of Akt/FOXO3a signaling. Increased levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) were also observed in hibernating bear serum. These observations suggest that protein metabolism in cultured human myotubes may be altered when incubated with hibernating bear serum, with a significant increase in serum IGF-1 and diminished MuRF1 expression, a potential target of Akt/FOXO3a signaling. A protein sparing phenotype in cultured muscle cells by treatment with hibernating bear serum holds potential for the development of methods to prevent human muscle atrophy and related disorders.
Read more »
 High-Flying Experiment: Do Stem Cells Grow Better in Space?Researcher Dhruv Sareen’s own stem cells are now orbiting the Earth. The mission? To test whether they’ll grow better in zero gravity.
High-Flying Experiment: Do Stem Cells Grow Better in Space?Researcher Dhruv Sareen’s own stem cells are now orbiting the Earth. The mission? To test whether they’ll grow better in zero gravity.
Read more »
 New Ford F-150 Raptor R is 700bhp super-truck | AutocarThe new FordPerformance F-150 Raptor R is one of the most extreme pick up trucks ever created
New Ford F-150 Raptor R is 700bhp super-truck | AutocarThe new FordPerformance F-150 Raptor R is one of the most extreme pick up trucks ever created
Read more »
 Scientists Created a New Solar Cell That Produces 1,000 Times More PowerSolar panels might one day be made from ferroelectric crystals instead of silicon. Researchers develop a layered format to increase the solar energy yield.
Scientists Created a New Solar Cell That Produces 1,000 Times More PowerSolar panels might one day be made from ferroelectric crystals instead of silicon. Researchers develop a layered format to increase the solar energy yield.
Read more »
 Scientists aim to grow billions of stem cells aboard the International Space StationThe researchers on a new space experiment hope to unlock a new method for growing billions of stem cells aboard the International Space Station.
Scientists aim to grow billions of stem cells aboard the International Space StationThe researchers on a new space experiment hope to unlock a new method for growing billions of stem cells aboard the International Space Station.
Read more »
