A Review in Molecular Neurodegeneration discusses the clinical and translational research on the connection between acute inflammatory insults and Alzheimer’s disease and the therapeutic approaches that may be used following inflammatory insults.
In the section that follows, we provide a roadmap for future research efforts directed at understanding the role that peripheral inflammatory insults may play in AD pathogenesis, and developing interventions to limit the deleterious effect these inflammatory stressors may have on brain health .
Extending this further, burgeoning evidence points to changes in the adaptive immune system in aging adults and adults with AD, with recent data showing that a portion of clonally expanded CD8 + T-cells in AD patients may be specifically reactive to the Epstein-Bar virus []; although outside the scope of this Roadmap paper, it will be important to clarify how acute inflammatory insults relate to chronic or latent infections, how acute infectious and non-infectious inflammatory insults impact...
Finally, another understudied area of research on acute inflammatory insults is how sex-based differences in immune response might serve as potential contributors to AD risk.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Molecular characterization of a flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene from citrus fruit reveals its crucial roles in anthocyanin accumulation - BMC Plant BiologyBackground Flavanone 3-hydroxylase (F3H), a key enzyme in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, plays an important role in the regulation of flavonols and anthocyanidins accumulation. Citrus fruit is a rich source of flavonoids with varied flavonoid compositions among different varieties. To date, the study on F3H is limited in citrus, and its roles in regulating flavonoid accumulation in citrus fruit are still unclear. Results In this study, we isolated a CitF3H from three different citrus varieties, Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.), Ponkan mandarin (C. reticulata Blanco) and blood orange ‘Moro’ (C. sinensis Osbeck). Functional analysis showed that CitF3H encoded a functional flavanone 3-hydroxylase. It catalyzed the hydroxylation of naringenin to yield dihydrokaempferol, which was a precursor of anthocyanins in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. In the juice sacs, CitF3H was differentially expressed among the three citrus varieties, and its expression level was positively correlated with the accumulation of anthocyanins during the ripening process. In the juice sacs of Satsuma mandarin and Ponkan mandarin the expression of CitF3H kept constant at an extremely low level, and no anthocyanin was accumulated during the ripening process. In contrast, the expression of CitF3H increased rapidly along with the accumulation of anthocyanin in the juice sacs of blood orange ‘Moro’ during the ripening process. In addition, we found that blue light irradiation was effective to up-regulate the expression of CitF3H and improve anthocyanin accumulation in the juice sacs of blood orange ‘Moro’ in vitro. Conclusion CitF3H was a key gene regulating anthocyanin accumulation in the juice sacs of citrus fruit. The results presented in this study will contribute to elucidating anthocyanin biosynthesis in citrus fruit, and provide new strategies to improve the nutritional and commercial values of citrus fruit.
Molecular characterization of a flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene from citrus fruit reveals its crucial roles in anthocyanin accumulation - BMC Plant BiologyBackground Flavanone 3-hydroxylase (F3H), a key enzyme in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, plays an important role in the regulation of flavonols and anthocyanidins accumulation. Citrus fruit is a rich source of flavonoids with varied flavonoid compositions among different varieties. To date, the study on F3H is limited in citrus, and its roles in regulating flavonoid accumulation in citrus fruit are still unclear. Results In this study, we isolated a CitF3H from three different citrus varieties, Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.), Ponkan mandarin (C. reticulata Blanco) and blood orange ‘Moro’ (C. sinensis Osbeck). Functional analysis showed that CitF3H encoded a functional flavanone 3-hydroxylase. It catalyzed the hydroxylation of naringenin to yield dihydrokaempferol, which was a precursor of anthocyanins in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. In the juice sacs, CitF3H was differentially expressed among the three citrus varieties, and its expression level was positively correlated with the accumulation of anthocyanins during the ripening process. In the juice sacs of Satsuma mandarin and Ponkan mandarin the expression of CitF3H kept constant at an extremely low level, and no anthocyanin was accumulated during the ripening process. In contrast, the expression of CitF3H increased rapidly along with the accumulation of anthocyanin in the juice sacs of blood orange ‘Moro’ during the ripening process. In addition, we found that blue light irradiation was effective to up-regulate the expression of CitF3H and improve anthocyanin accumulation in the juice sacs of blood orange ‘Moro’ in vitro. Conclusion CitF3H was a key gene regulating anthocyanin accumulation in the juice sacs of citrus fruit. The results presented in this study will contribute to elucidating anthocyanin biosynthesis in citrus fruit, and provide new strategies to improve the nutritional and commercial values of citrus fruit.
Read more »
 A history of repeated alcohol intoxication promotes cognitive impairment and gene expression signatures of disease progression in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer’s diseaseThe impact of alcohol abuse on Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is poorly understood. Here, we show that the onset of neurocognitive impairment in a mouse model of AD is hastened by repeated alcohol intoxication through exposure to alcohol vapor, and we provide a comprehensive gene expression dataset of the prefrontal cortex by the single-nucleus RNA sequencing of 113,242 cells. We observed a broad dysregulation of gene expression that involves neuronal excitability, neurodegeneration, and inflammation, including interferon genes. Several genes previously associated with AD in humans by genome-wide association studies were differentially regulated in specific neuronal populations. Gene expression patterns of AD mice with a history of alcohol intoxication were more similar to gene expression signatures of older AD mice with more advanced disease and cognitive impairment than those of younger AD mice with prodromic disease, suggesting that alcohol promotes transcriptional changes consistent with AD progression. Our gene expression dataset at the single-cell level provides a unique resource for investigations of the molecular bases of the detrimental role of excessive alcohol intake in AD. Significance statement Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease worldwide. Many efforts have been geared toward the identification of environmental and genetic risk factors. However, alcohol has received limited attention as a potential risk factor for AD. We explored effects of the interaction of a history of alcohol intoxication with genetic AD susceptibility on cognitive performance and gene expression at the single-cell level. We found that a history of repeated alcohol intoxication promotes the emergence of spatial learning and memory impairments in pre-symptomatic triple transgenic AD (3xTg-AD) mice. We also show that a history of repeated alcohol intoxication induces prefrontal cortex transcriptional changes associated with AD progression.
A history of repeated alcohol intoxication promotes cognitive impairment and gene expression signatures of disease progression in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer’s diseaseThe impact of alcohol abuse on Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is poorly understood. Here, we show that the onset of neurocognitive impairment in a mouse model of AD is hastened by repeated alcohol intoxication through exposure to alcohol vapor, and we provide a comprehensive gene expression dataset of the prefrontal cortex by the single-nucleus RNA sequencing of 113,242 cells. We observed a broad dysregulation of gene expression that involves neuronal excitability, neurodegeneration, and inflammation, including interferon genes. Several genes previously associated with AD in humans by genome-wide association studies were differentially regulated in specific neuronal populations. Gene expression patterns of AD mice with a history of alcohol intoxication were more similar to gene expression signatures of older AD mice with more advanced disease and cognitive impairment than those of younger AD mice with prodromic disease, suggesting that alcohol promotes transcriptional changes consistent with AD progression. Our gene expression dataset at the single-cell level provides a unique resource for investigations of the molecular bases of the detrimental role of excessive alcohol intake in AD. Significance statement Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease worldwide. Many efforts have been geared toward the identification of environmental and genetic risk factors. However, alcohol has received limited attention as a potential risk factor for AD. We explored effects of the interaction of a history of alcohol intoxication with genetic AD susceptibility on cognitive performance and gene expression at the single-cell level. We found that a history of repeated alcohol intoxication promotes the emergence of spatial learning and memory impairments in pre-symptomatic triple transgenic AD (3xTg-AD) mice. We also show that a history of repeated alcohol intoxication induces prefrontal cortex transcriptional changes associated with AD progression.
Read more »
 Daisy Hill Hospital: Campaigners meet senior health officialsCampaigners aiming to protect services at Daisy Hill Hospital met senior healthdpt officials earlier at Stormont
Daisy Hill Hospital: Campaigners meet senior health officialsCampaigners aiming to protect services at Daisy Hill Hospital met senior healthdpt officials earlier at Stormont
Read more »
 Connecting the inflammatory dots: Obesity, depression, and Alzheimer's linked by neuroinflammationObesity-induced neuroinflammation significantly contributes to the pathophysiology of depression and Alzheimer's disease. Targeting midlife stage for intervention is crucial to potentially prevent Alzheimer's pathology.
Connecting the inflammatory dots: Obesity, depression, and Alzheimer's linked by neuroinflammationObesity-induced neuroinflammation significantly contributes to the pathophysiology of depression and Alzheimer's disease. Targeting midlife stage for intervention is crucial to potentially prevent Alzheimer's pathology.
Read more »
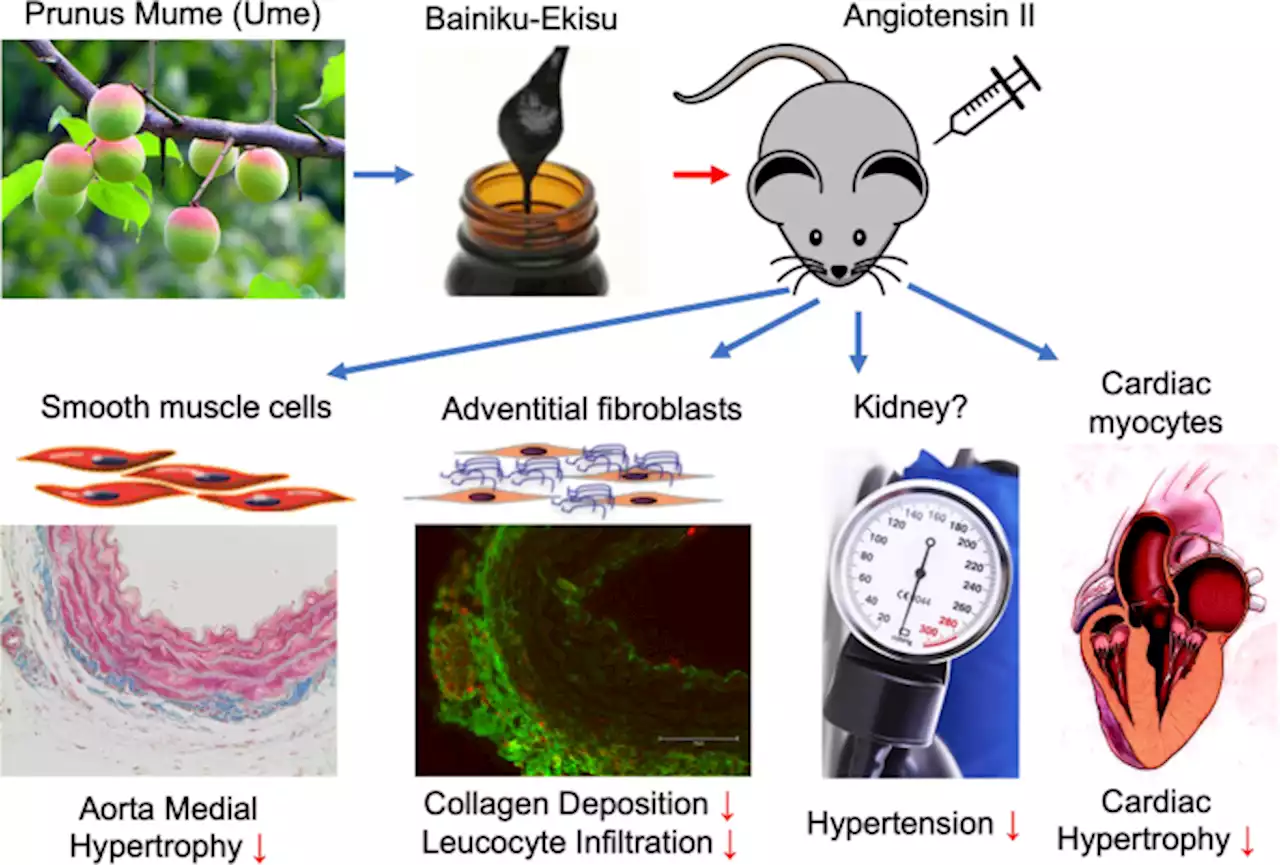 Infused juice concentrate of Japanese plum Prunus mume attenuates inflammatory vascular remodeling in a mouse model of hypertension induced by angiotensin II - Hypertension ResearchHypertension Research - Infused juice concentrate of Japanese plum Prunus mume attenuates inflammatory vascular remodeling in a mouse model of hypertension induced by angiotensin II
Infused juice concentrate of Japanese plum Prunus mume attenuates inflammatory vascular remodeling in a mouse model of hypertension induced by angiotensin II - Hypertension ResearchHypertension Research - Infused juice concentrate of Japanese plum Prunus mume attenuates inflammatory vascular remodeling in a mouse model of hypertension induced by angiotensin II
Read more »
 Bamboo's hidden treasures: unveiling the possible health-boosting powers of leaf and sheath extractsBamboo's hidden treasures: unveiling the possible health-boosting powers of leaf and sheath extracts antioxidants_OA UniCalPortale bamboo leaf sheath extract antoxidant antiinfammatory
Bamboo's hidden treasures: unveiling the possible health-boosting powers of leaf and sheath extractsBamboo's hidden treasures: unveiling the possible health-boosting powers of leaf and sheath extracts antioxidants_OA UniCalPortale bamboo leaf sheath extract antoxidant antiinfammatory
Read more »