Study sheds light on how scramblase proteins rearrange cell membranes cornell NatureComms
. For wiltype and mutant afTMEM16 the leak is >2 orders of magnitude smaller than the rate constant of protein-mediated scrambling and therefore is negligible. All conditions were tested side by side with a control preparation of WT afTMEM16 reconstituted in C18 lipids. In some rare cases this control sample behaved anomalously, judged by scrambling fit parameters outside 3 times the standard deviation of the mean for the wildtype.
. Briefly, MSP1E3 in a pET vector was transformed into the BL21-Gold strain . Transformed cells were grown in LB media supplemented with Kanamycin to an ODof 0.8 and expression was induced with 1 mM IPTG for 3 h. Cells were harvested and resuspended in 40 mM Tris-HCl pH 78.0, 300 mM NaCl supplemented with 1% Triton X-100, 5 μg mlpepstatin, 100 μM phenylmethane sulphonylfluoride and protease inhibitor cocktail tablets .
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Versatile strategy for homogeneous drying patterns of dispersed particles - Nature CommunicationsCoating technologies call for effective methods capable of suppressing the coffee-ring effect for a uniform particle deposition. Rey et al. show homogeneous drying patterns can be achieved via physically adsorbing polymers onto particle surfaces and the method is applicable to a wide range of materials regardless of the shape of the dispersed particles.
Versatile strategy for homogeneous drying patterns of dispersed particles - Nature CommunicationsCoating technologies call for effective methods capable of suppressing the coffee-ring effect for a uniform particle deposition. Rey et al. show homogeneous drying patterns can be achieved via physically adsorbing polymers onto particle surfaces and the method is applicable to a wide range of materials regardless of the shape of the dispersed particles.
Read more »
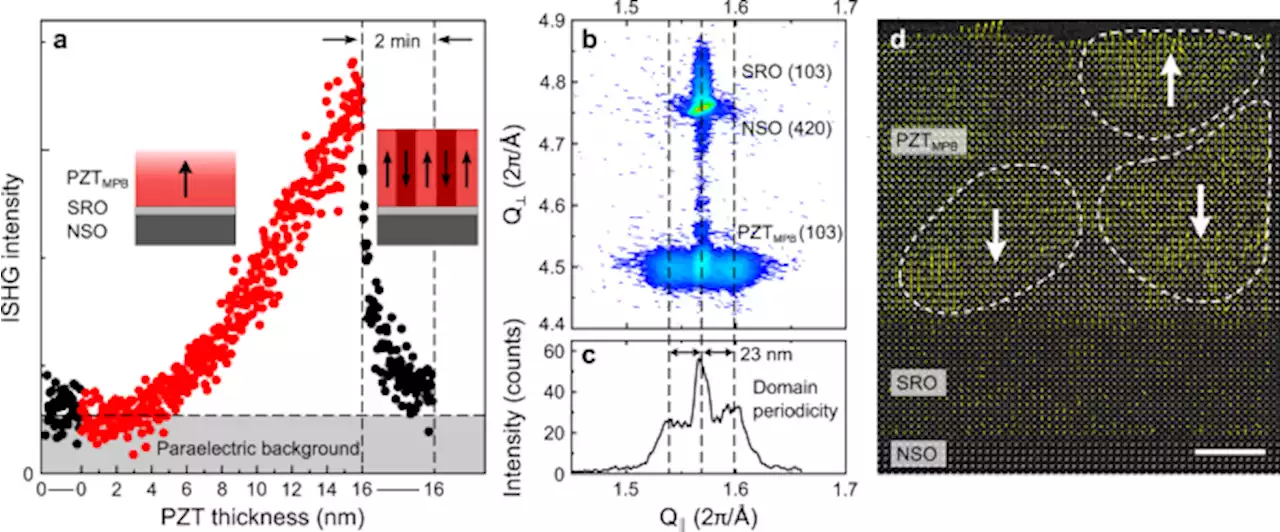 Multilevel polarization switching in ferroelectric thin films - Nature CommunicationsSetting any polarization value in ferroelectric thin films is a key step for their implementation in neuromorphic devices. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous modulation of the remanent polarization at the nanoscale in PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 films.
Multilevel polarization switching in ferroelectric thin films - Nature CommunicationsSetting any polarization value in ferroelectric thin films is a key step for their implementation in neuromorphic devices. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous modulation of the remanent polarization at the nanoscale in PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 films.
Read more »
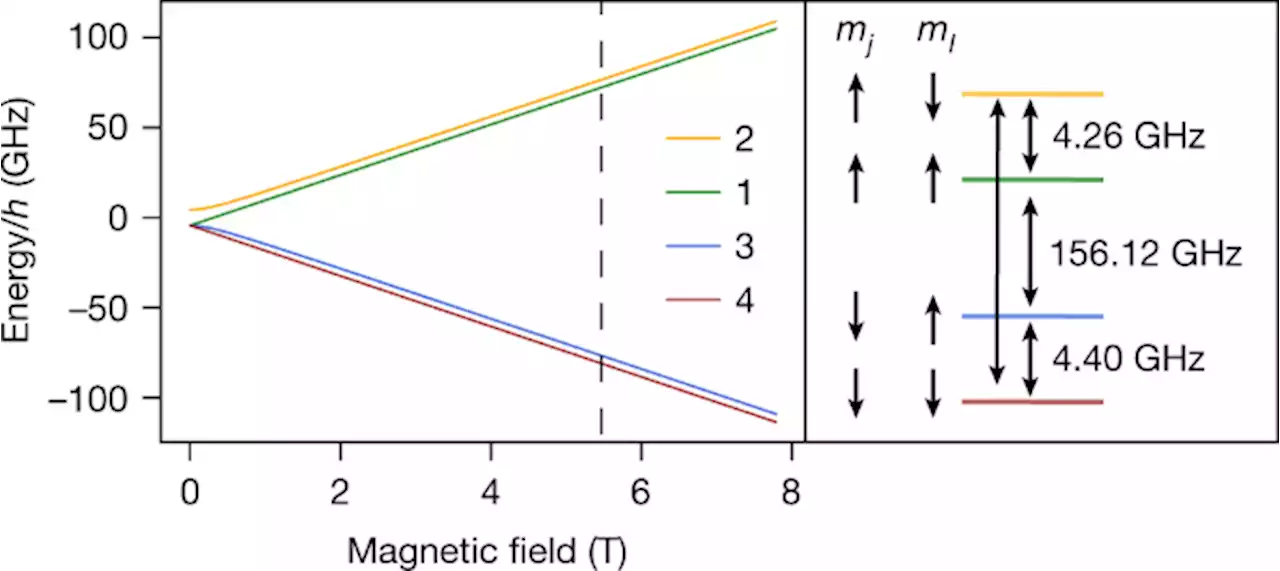 Direct measurement of the 3He+ magnetic moments - NatureMeasuring the hyperfine structure of a single helium-3 ion in a Penning trap enables direct measurement of the nuclear magnetic moment of helium-3 and provides the high accuracy needed for NMR-based magnetometry.
Direct measurement of the 3He+ magnetic moments - NatureMeasuring the hyperfine structure of a single helium-3 ion in a Penning trap enables direct measurement of the nuclear magnetic moment of helium-3 and provides the high accuracy needed for NMR-based magnetometry.
Read more »
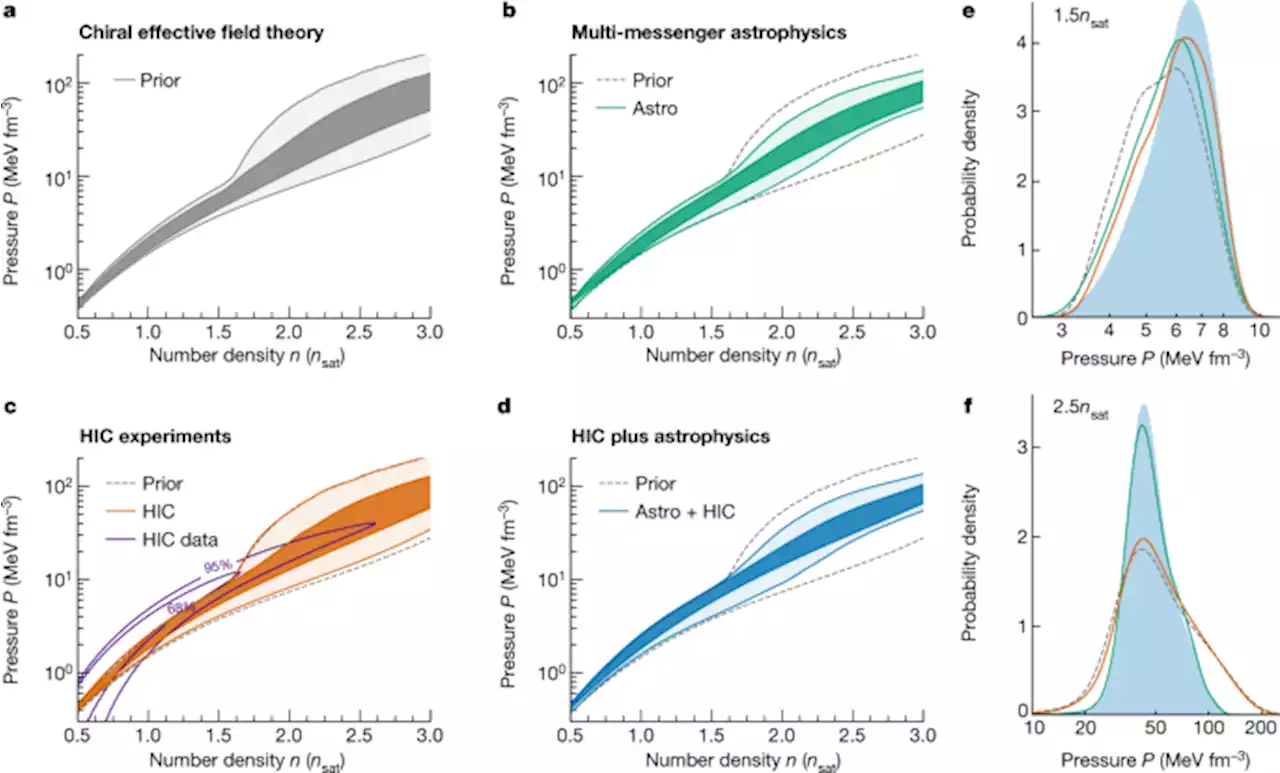 Constraining neutron-star matter with microscopic and macroscopic collisions - NatureThe physics of dense matter extracted from neutron star collision data is demonstrated to be consistent with information obtained from heavy-ion collisions, and analyses incorporating both data sources as well as information from nuclear theory provide new constraints for neutron star matter.
Constraining neutron-star matter with microscopic and macroscopic collisions - NatureThe physics of dense matter extracted from neutron star collision data is demonstrated to be consistent with information obtained from heavy-ion collisions, and analyses incorporating both data sources as well as information from nuclear theory provide new constraints for neutron star matter.
Read more »
 Indian Regulator: Crypto's Decentralized Nature Makes Regulation Challenging – Bitcoin NewsIndia's market regulator says the decentralized nature of crypto assets makes consumer protection and regulatory enforcement challenging. cryptocurrency bitcoin
Indian Regulator: Crypto's Decentralized Nature Makes Regulation Challenging – Bitcoin NewsIndia's market regulator says the decentralized nature of crypto assets makes consumer protection and regulatory enforcement challenging. cryptocurrency bitcoin
Read more »
 Sub-aerial talik formation observed across the discontinuous permafrost zone of Alaska - Nature GeoscienceTemperature observations from across Alaska show widespread talik formation in the discontinuous permafrost zone due to higher air temperatures and above-average snowfall in recent years.
Sub-aerial talik formation observed across the discontinuous permafrost zone of Alaska - Nature GeoscienceTemperature observations from across Alaska show widespread talik formation in the discontinuous permafrost zone due to higher air temperatures and above-average snowfall in recent years.
Read more »
