Researchers have discovered a new species of marine bacteria that reproduces through a unique budding process and releases viruses to facilitate nitrogen metabolism. Researchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed. The study, recently p
, which is unique for its budding division model and plays a significant role in nitrogen assimilation. The bacteria also live symbiotically with a bacteriophage that further facilitates nitrogen metabolism.
Researchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed., is hailed by the editors as a significant contribution to our grasp of the physiological processes within deep-seabacteria.
bacteria are known to reside, and then encouraged their growth by supplementing a standard growth medium with the antibiotic rifampicin and sources of nitrogen. They cultured these enriched bacteria on agar and evaluated individual colonies further by gene sequencing. They also discovered that the addition of nitrate or ammonia caused the novel strain to release a bacteriophage – a type of virus that infects bacteria. Bacteriophages are widely distributed across oceans and can regulate nitrogen metabolism in their host bacteria. This bacteriophage – called phage-ZRK32 – was able to increase the growth ofand other marine bacteria dramatically by facilitating nitrogen metabolism.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 New species of marine bacteria isolated from a deep-sea cold seepResearchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed.
New species of marine bacteria isolated from a deep-sea cold seepResearchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed.
Read more »
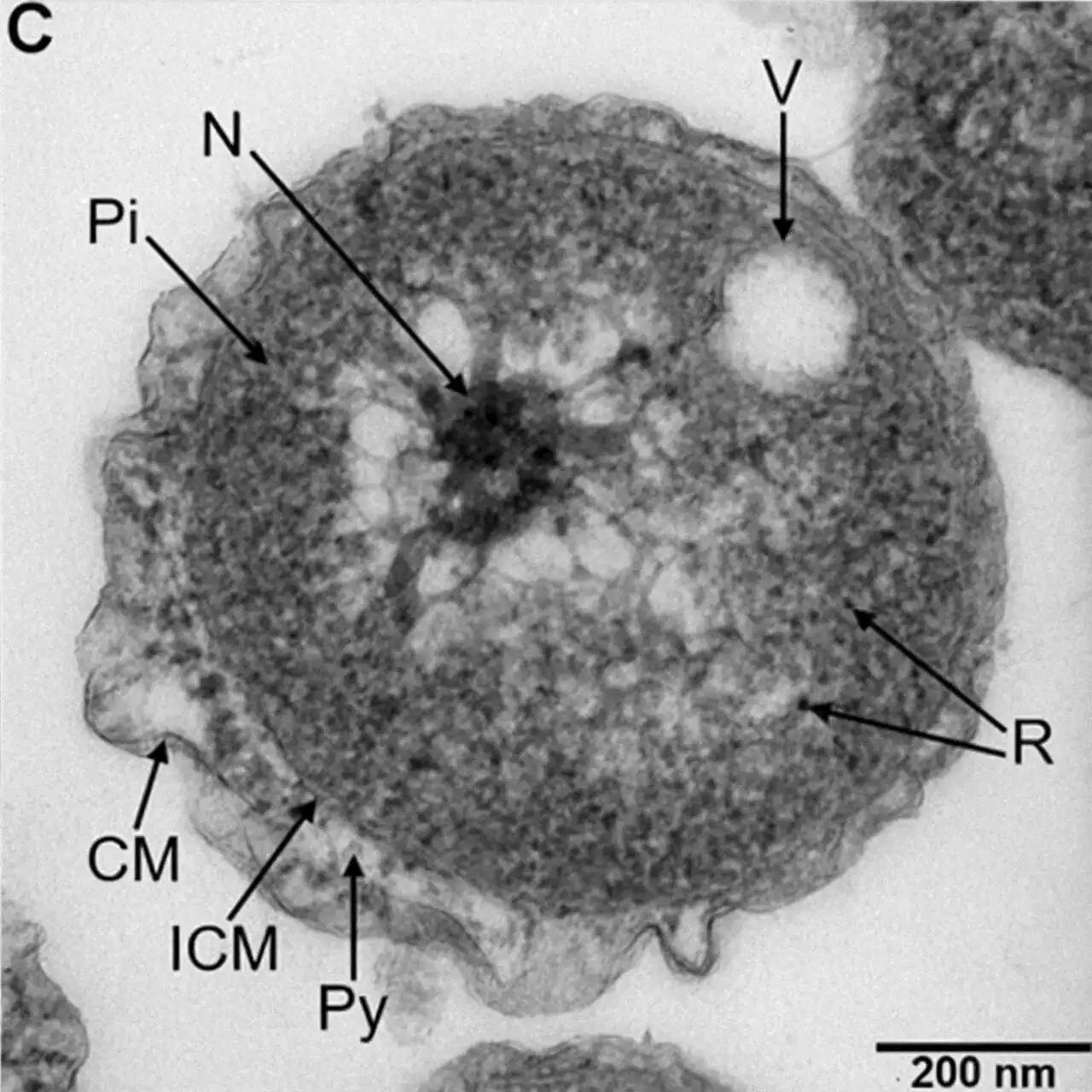 New species of marine bacteria isolated from a deep-sea cold seepResearchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed.
New species of marine bacteria isolated from a deep-sea cold seepResearchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed.
Read more »
 New Aristolochiaceae liana species found in Yunnan, ChinaTraditionally, the genus Aristolochia L. sensu lato is the largest genus in the family Aristolochiaceae. According to recent morphological and phylogenetic studies, Aristolochia subgen. Siphisia has been reintroduced as a separate genus Isotrema.
New Aristolochiaceae liana species found in Yunnan, ChinaTraditionally, the genus Aristolochia L. sensu lato is the largest genus in the family Aristolochiaceae. According to recent morphological and phylogenetic studies, Aristolochia subgen. Siphisia has been reintroduced as a separate genus Isotrema.
Read more »
 Scientists Discover 7 “Cryptic” New Species of Walking LeavesAn international team of scientists, including researchers from the University of Göttingen, has unveiled seven new species of leaf insects, commonly known as walking leaves. A team of international researchers, including experts from the University of Göttingen, has identified seven new species of
Scientists Discover 7 “Cryptic” New Species of Walking LeavesAn international team of scientists, including researchers from the University of Göttingen, has unveiled seven new species of leaf insects, commonly known as walking leaves. A team of international researchers, including experts from the University of Göttingen, has identified seven new species of
Read more »
 Good News Everyone: We Found a New Species of Roundworm That Can Infect Our BrainsIn a report this week, doctors have documented the first case of a human brain infection caused by a roundworm normally found in Australian snakes.
Good News Everyone: We Found a New Species of Roundworm That Can Infect Our BrainsIn a report this week, doctors have documented the first case of a human brain infection caused by a roundworm normally found in Australian snakes.
Read more »
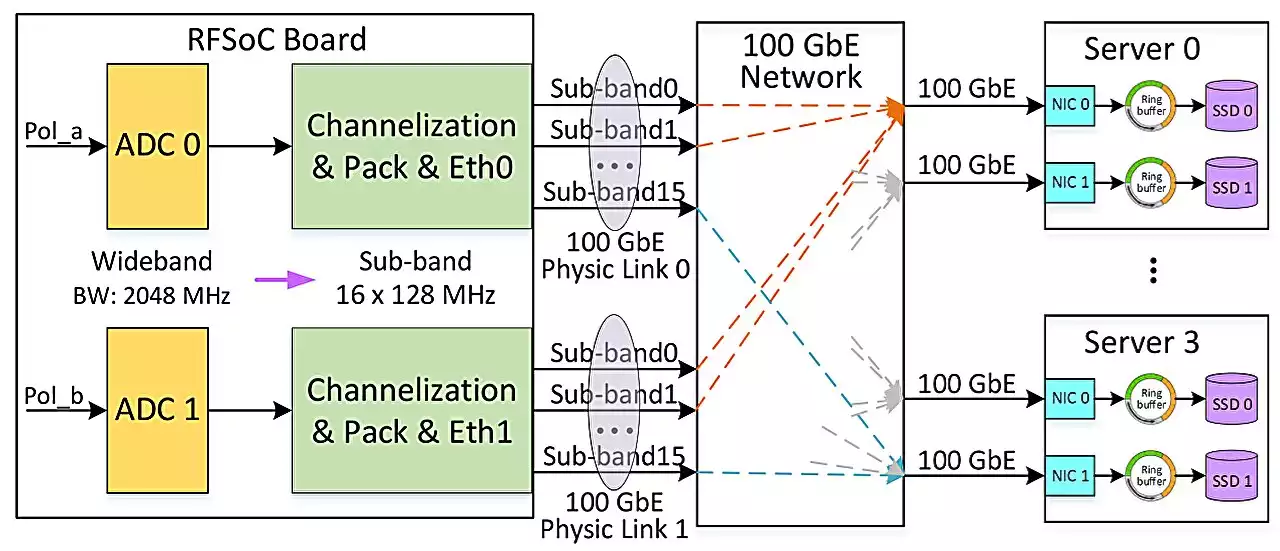 Researchers propose new technology to improve observation sensitivity of QiTai radio telescopeThe world's most powerful steerable 110-meter radio telescope, also known as the QiTai radio Telescope (QTT), will be built by Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) over a period of six years. Its ceremony kicked off on Sept. 21, 2022.
Researchers propose new technology to improve observation sensitivity of QiTai radio telescopeThe world's most powerful steerable 110-meter radio telescope, also known as the QiTai radio Telescope (QTT), will be built by Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) over a period of six years. Its ceremony kicked off on Sept. 21, 2022.
Read more »