Science, Space and Technology News 2023
We and our partners use cookies to Store and/or access information on a device. We and our partners use data for Personalised ads and content, ad and content measurement, audience insights and product development. An example of data being processed may be a unique identifier stored in a cookie. Some of our partners may process your data as a part of their legitimate business interest without asking for consent.
The research is part of an ongoing effort by Si, who won a prestigious Vannevar Bush Faculty Fellowship from the Defense Department in July to pursue the validation of a theoretical framework for controlling topological states of matter.In the study, Si and Hu showed that electrons from d atomic orbitals could become part of larger, molecular orbitals that are shared by several atoms in the lattice.
“This dirt road lies so far from the highway,” he said. “The influence from the highway is very small, which translates to a minute energy scale and very low-temperature physics. This means you need to go to temperatures around 10 Kelvin or so to even see the effects of coupling. “Even when it has faded into a dirt road, it still shares status with the other lanes, because they all came from the d orbital,” Si said. “It is effectively a dirt road, but it is much more strongly coupled, and that translates to physics at much higher temperatures.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Unraveling The Infostealer ThreatMike Wilson is the Founder & CTO of Enzoic, a cybersecurity company that helps prevent account takeover of employee and customer accounts. Read Mike Wilson's full executive profile here.
Unraveling The Infostealer ThreatMike Wilson is the Founder & CTO of Enzoic, a cybersecurity company that helps prevent account takeover of employee and customer accounts. Read Mike Wilson's full executive profile here.
Read more »
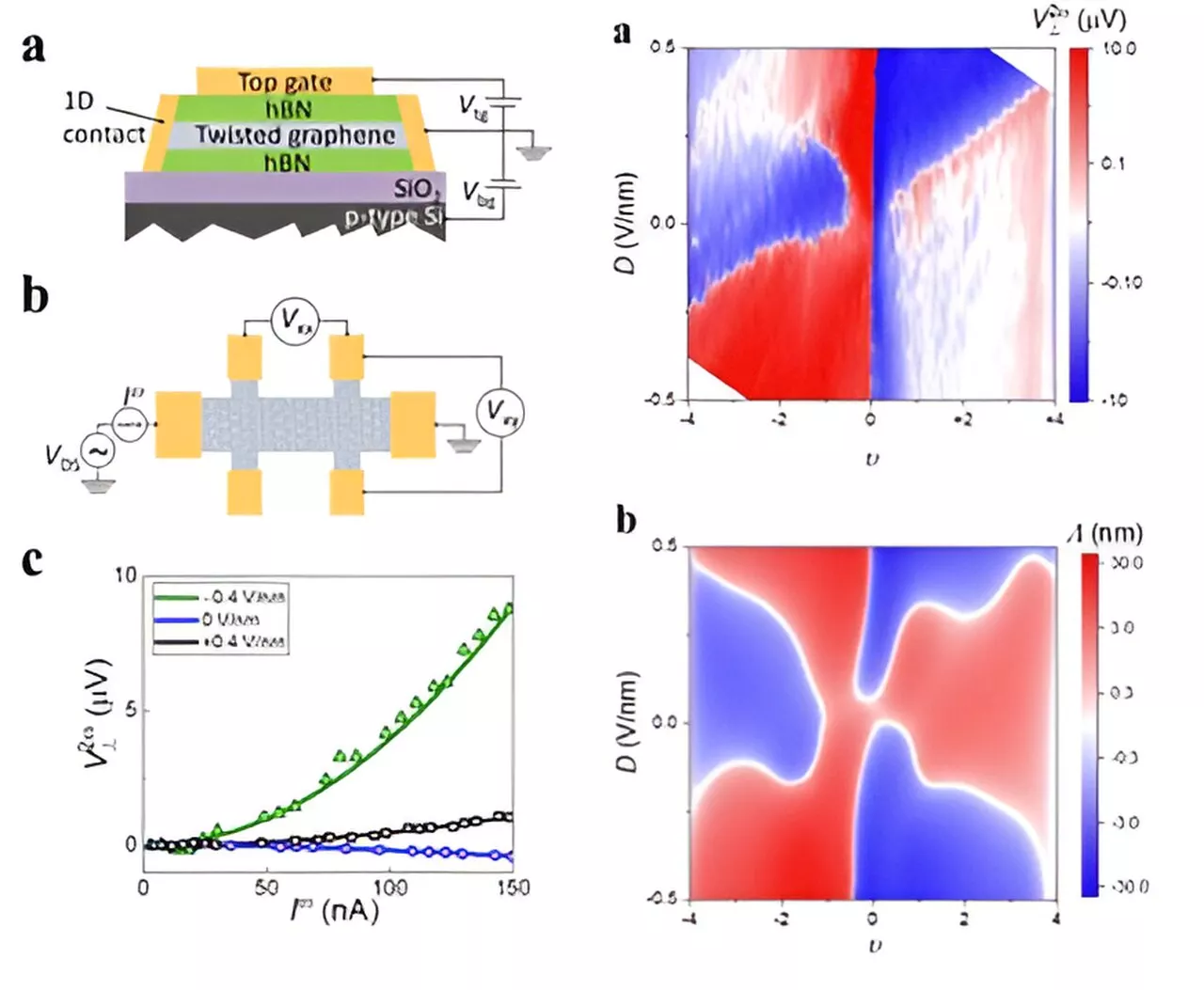 Physicists unlock controllable nonlinear Hall effect in twisted bilayer grapheneA team of international researchers led by The University of Hong Kong (HKU) and The University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has made a significant discovery in the field of quantum materials, uncovering the controllable nonlinear Hall effect in twisted bilayer graphene.
Physicists unlock controllable nonlinear Hall effect in twisted bilayer grapheneA team of international researchers led by The University of Hong Kong (HKU) and The University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has made a significant discovery in the field of quantum materials, uncovering the controllable nonlinear Hall effect in twisted bilayer graphene.
Read more »
 A new way to erase quantum computer errorsResearchers have demonstrated a type of quantum eraser. The physicists show that they can pinpoint and correct for mistakes in quantum computing systems known as 'erasure' errors.
A new way to erase quantum computer errorsResearchers have demonstrated a type of quantum eraser. The physicists show that they can pinpoint and correct for mistakes in quantum computing systems known as 'erasure' errors.
Read more »
 Exploring parameter shift for quantum Fisher informationIn a recent publication in EPJ Quantum Technology, Le Bin Ho from Tohoku University's Frontier Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences has developed a technique called time-dependent stochastic parameter shift in the realm of quantum computing and quantum machine learning. This breakthrough method revolutionizes the estimation of gradients or derivatives of functions, a crucial step in many computational tasks.
Exploring parameter shift for quantum Fisher informationIn a recent publication in EPJ Quantum Technology, Le Bin Ho from Tohoku University's Frontier Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences has developed a technique called time-dependent stochastic parameter shift in the realm of quantum computing and quantum machine learning. This breakthrough method revolutionizes the estimation of gradients or derivatives of functions, a crucial step in many computational tasks.
Read more »
 The quantum experiment that could help find evidence of the multiverseScars of collisions with other universes could show up in radiation from the big bang. A new experiment aims to mimic these collisions and help us look for them
The quantum experiment that could help find evidence of the multiverseScars of collisions with other universes could show up in radiation from the big bang. A new experiment aims to mimic these collisions and help us look for them
Read more »
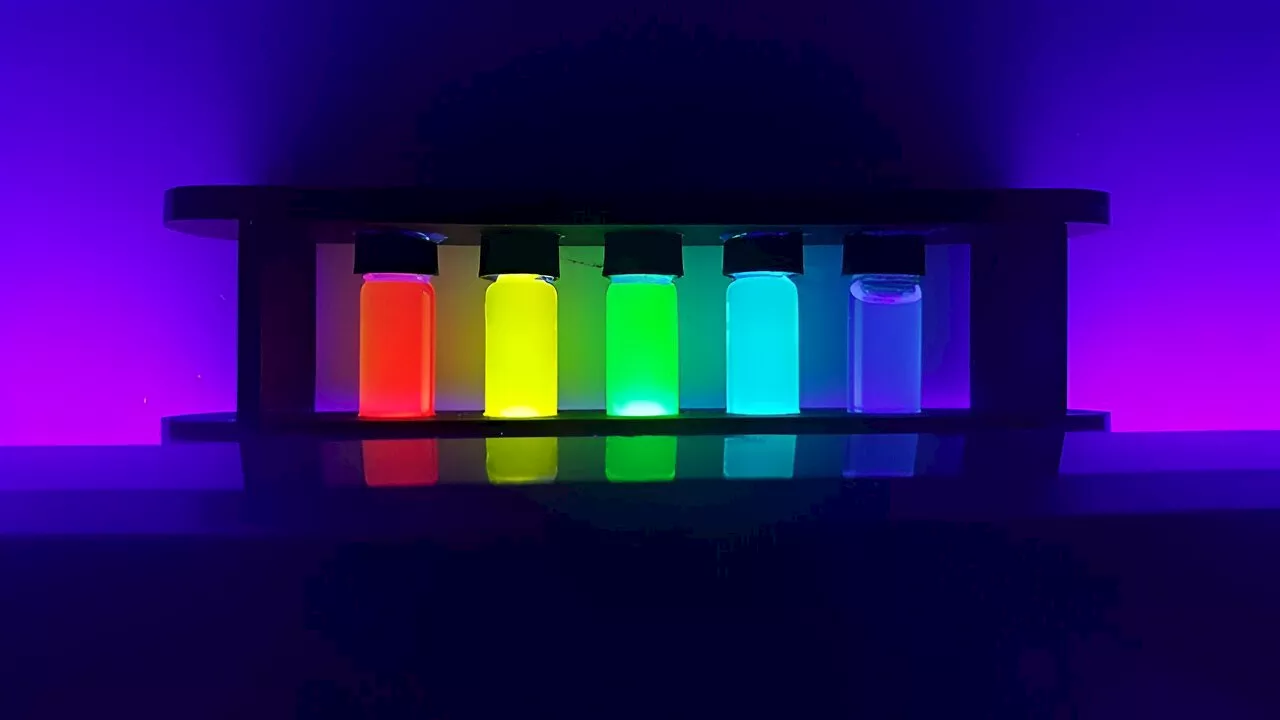 Q&A: Expert discusses past and future of Nobel-winning quantum dots technologyThe world woke up on Oct. 3 to learn that Moungi Bawendi of MIT, Louis Brus of Columbia University, and Alexei Ekimov of Nanocrystals Inc. received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their discovery and synthesis of semiconductor quantum dots.
Q&A: Expert discusses past and future of Nobel-winning quantum dots technologyThe world woke up on Oct. 3 to learn that Moungi Bawendi of MIT, Louis Brus of Columbia University, and Alexei Ekimov of Nanocrystals Inc. received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their discovery and synthesis of semiconductor quantum dots.
Read more »
