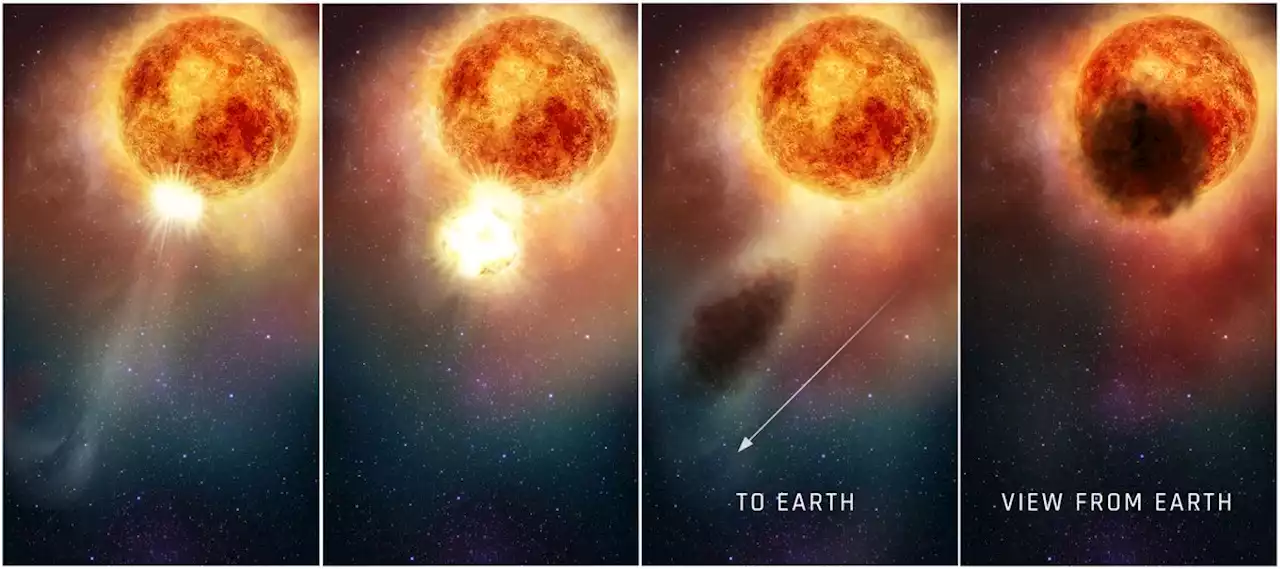
Why Betelgeuse Dimmed universetoday storybywill
. These observations revealed that in 2019, Beteleguese “blew its stack” and released a tremendous amount of material into space.
Like a CME, this massive ejection was likely caused by a buoyant jet of superheated material bubbling up from deep inside the star . This plume is estimated to have been measured more than a million kilometers across and several times as mass as our Moon. So great were the shocks and pulsations that it was enough to blast off a sizeable patch of material from Betelgeuse’s outer shell .
What’s more, the shock caused by this event is something Betelgeuse still hasn’t fully recovered from. The supergiant’s 400-day pulsation rate is now gone , something astronomers have not seen in almost 200 years of observations. The sudden disappearance of this variability in brightness and surface motions is further evidence of how disruptive this blowout was. As Dupree explained in a recent NASA“Betelgeuse continues doing some very unusual things right now; the interior is sort of bouncing.
This illustration plots changes in the brightness of the red supergiant star Betelgeuse, following the titanic mass ejection of a large piece of its visible surface. Credits: NASA/ESA/Elizabeth Wheatley These observations could yield fresh clues about how red stars lose mass late in their lives as their nuclear fuel is slowly exhausted, eventually culminating in a supernova. How much mass they shed as they near the end of their Red Giant phase would have a significant effect on their fate. In addition, the way this event completely dwarfs ejections from the Sun’s corona could suggest that SMEs and CMEs are separate classes of stellar events.
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Hubble Sees Red Supergiant Star Betelgeuse Recovering After Never-Seen-Before Titanic EruptionMonster Star Had Never-Seen-Before Titanic Eruption Betelgeuse, a red supergiant star, appears as a brilliant, ruby-red, twinkling spot of light in the upper right shoulder of the winter constellation Orion the Hunter. However, when viewed close up, astronomers know that it is a seething mons
Hubble Sees Red Supergiant Star Betelgeuse Recovering After Never-Seen-Before Titanic EruptionMonster Star Had Never-Seen-Before Titanic Eruption Betelgeuse, a red supergiant star, appears as a brilliant, ruby-red, twinkling spot of light in the upper right shoulder of the winter constellation Orion the Hunter. However, when viewed close up, astronomers know that it is a seething mons
Read more »
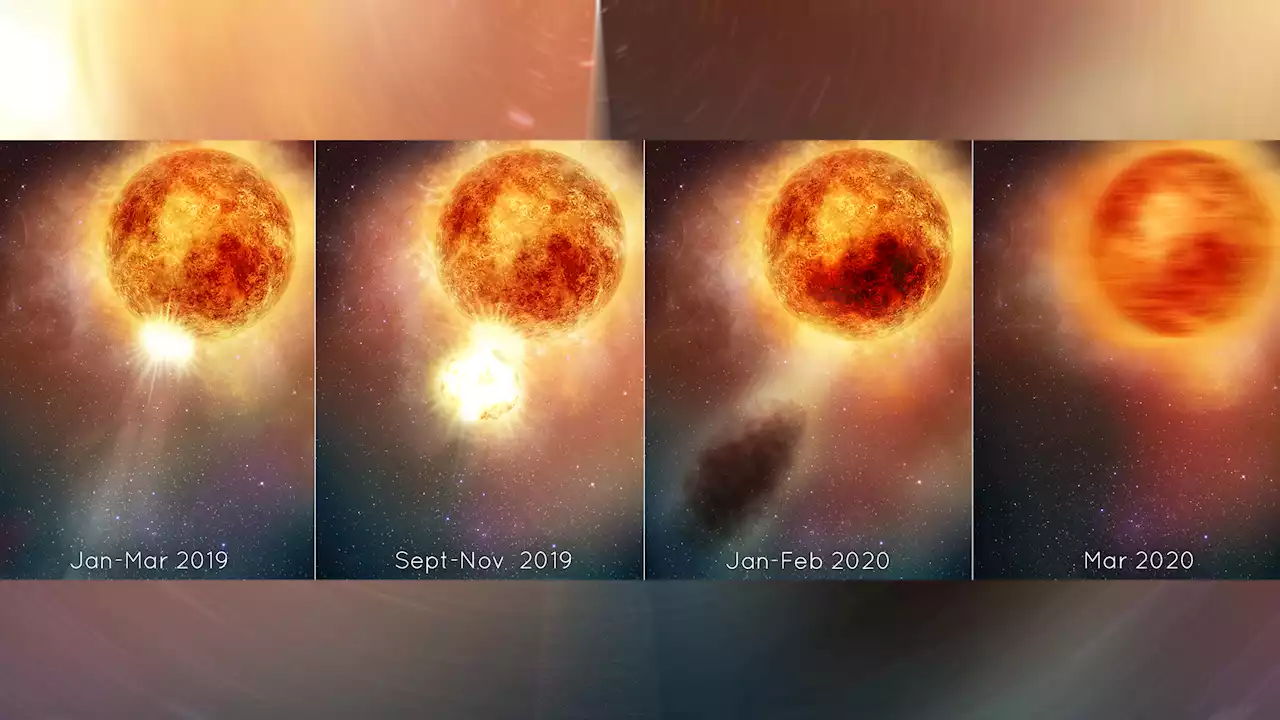 Hubble catches red supergiant star Betelgeuse recovering after blowing its topAfter losing several million moons in mass in 2019, Betelgeuse has been observed apparently attempting to heal itself.
Hubble catches red supergiant star Betelgeuse recovering after blowing its topAfter losing several million moons in mass in 2019, Betelgeuse has been observed apparently attempting to heal itself.
Read more »
 Hubble-servicing NASA astronaut urges human-robot synergy for future moon missions'All robotic exploration is really a human-robotic partnership. How do we amplify the science in this human-robotic partnership?'
Hubble-servicing NASA astronaut urges human-robot synergy for future moon missions'All robotic exploration is really a human-robotic partnership. How do we amplify the science in this human-robotic partnership?'
Read more »
 Hubble just captured this dazzling image of a star clusterThe latest Hubble image captures a mind-blowing star cluster found in the Sagittarius constellation and proves it still has plenty of life.
Hubble just captured this dazzling image of a star clusterThe latest Hubble image captures a mind-blowing star cluster found in the Sagittarius constellation and proves it still has plenty of life.
Read more »
 Five Local Arts Events Using the Human Form as InspirationFive local arts events using the human form as inspiration.
Five Local Arts Events Using the Human Form as InspirationFive local arts events using the human form as inspiration.
Read more »
