A Research article published in Crit_Care reports an association between corticosteroid use and intensive care unit-acquired infection in critically ill COVID-19 patients.
We want to thank Guy Francois of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine for his support.
Dept of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Ghent University, Ghent, BelgiumAri Ercole & Alasdair Jubb Department of Intensive Care, Amsterdam UMC Location Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The NetherlandsLaboratory for Critical Care Computational Intelligence, Amsterdam Medical Data Science, Amsterdam UMC, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, The NetherlandsCenter for Clinical Epidemiology and Research Unit of Clinical Epidemiology, OUH Odense University Hospital, Odense, DenmarkPolyvalent Intensive Care Unit, Hospital de São Francisco Xavier, CHLO, Lisbon, Portugal2Nd Critical Care...
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Antibodies in the breastmilk of COVID-19 recovered women - BMC Pregnancy and ChildbirthObjective Human milk contains antibodies against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) which may serve as a protective factor through passive immunization in infants. The objective of this study was to measure the levels of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgA in human milk and serum after a SARS-CoV-2 infection. Design Breast milk and serum samples from 72 lactating mothers with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic or symptomatic infection were collected 1-229 days after the onset of clinical symptoms related to COVID-19. Seventeen mothers with no history of COVID-19 served as a control group. Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay was performed to analyze antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Results SARS-CoV-2-IgA human milk antibodies were detected in mothers and their concentrations were consistently higher than SARS-CoV-2-IgG antibodies. The serum and breastmilk samples of women with COVID-19 was characterized by a higher concentration of anti-RBD IgA and IgG than the serum from the control group without COVID-19. No statistically significant difference was observed between the antibody levels in the serum samples obtained from symptomatic and asymptomatic women exposed to SARS-CoV-2 and between the antibody level and the time from a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result over the period studied. Conclusion Our results confirm the presence of SARS-CoV-2 IgA and IgG antibodies in the breastmilk of COVID-19 recovered women and the possibility of these antibodies in providing specific immunologic benefits to breastfeeding infants such as protection against the virus transmission and severity of the acquired COVID-19 disease.
Antibodies in the breastmilk of COVID-19 recovered women - BMC Pregnancy and ChildbirthObjective Human milk contains antibodies against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) which may serve as a protective factor through passive immunization in infants. The objective of this study was to measure the levels of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgA in human milk and serum after a SARS-CoV-2 infection. Design Breast milk and serum samples from 72 lactating mothers with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic or symptomatic infection were collected 1-229 days after the onset of clinical symptoms related to COVID-19. Seventeen mothers with no history of COVID-19 served as a control group. Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay was performed to analyze antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Results SARS-CoV-2-IgA human milk antibodies were detected in mothers and their concentrations were consistently higher than SARS-CoV-2-IgG antibodies. The serum and breastmilk samples of women with COVID-19 was characterized by a higher concentration of anti-RBD IgA and IgG than the serum from the control group without COVID-19. No statistically significant difference was observed between the antibody levels in the serum samples obtained from symptomatic and asymptomatic women exposed to SARS-CoV-2 and between the antibody level and the time from a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result over the period studied. Conclusion Our results confirm the presence of SARS-CoV-2 IgA and IgG antibodies in the breastmilk of COVID-19 recovered women and the possibility of these antibodies in providing specific immunologic benefits to breastfeeding infants such as protection against the virus transmission and severity of the acquired COVID-19 disease.
Read more »
 Covid booster rollout to start in England this September - who’s eligible?The Covid Autumn booster will be available for 5 September
Covid booster rollout to start in England this September - who’s eligible?The Covid Autumn booster will be available for 5 September
Read more »
 Grieving mum remembers son who lost battle with Covid aged 36'I didn't realise how happy my son made me until the day he left this planet'
Grieving mum remembers son who lost battle with Covid aged 36'I didn't realise how happy my son made me until the day he left this planet'
Read more »
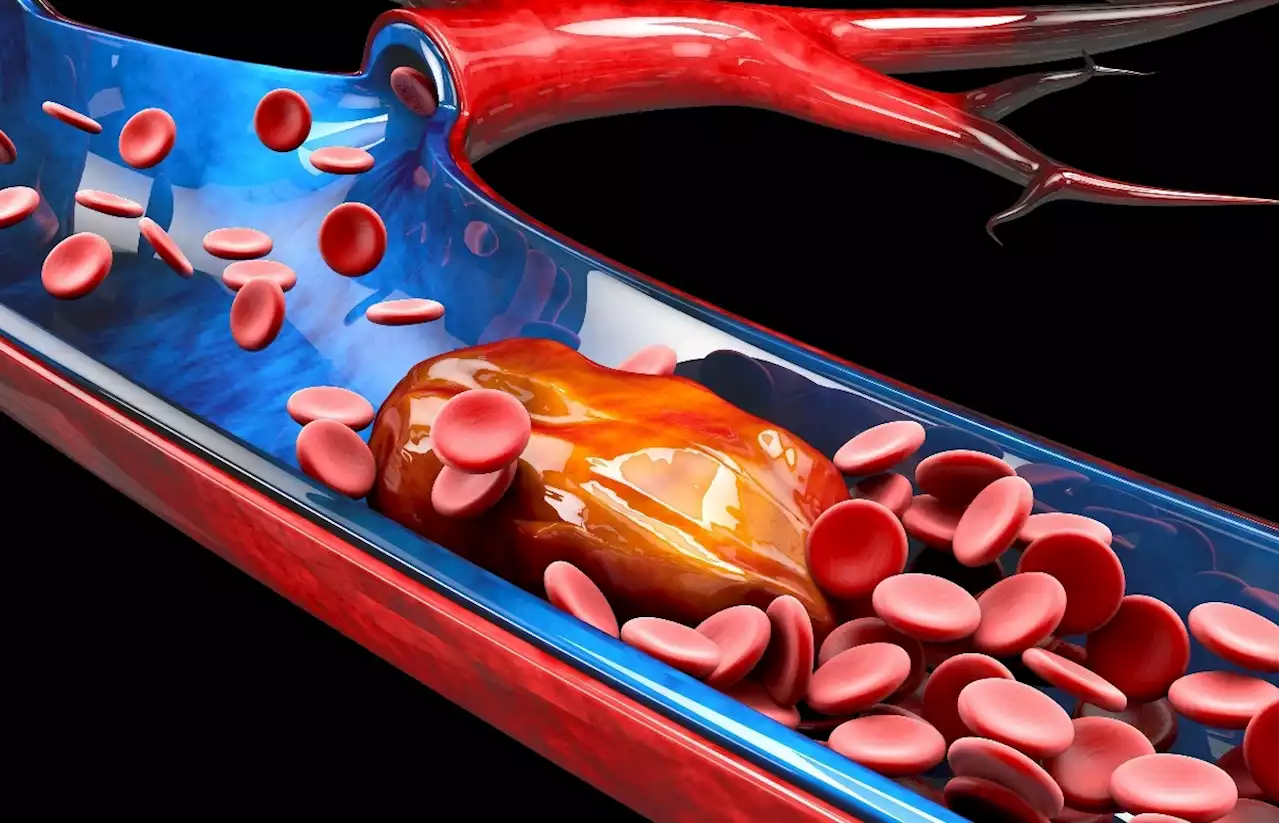 What is the association between COVID-19 and thrombotic events?What is the association between COVID-19 and thrombotic events? COVID19 ThromboticEvents SARSCoV2 Influenza Penn
What is the association between COVID-19 and thrombotic events?What is the association between COVID-19 and thrombotic events? COVID19 ThromboticEvents SARSCoV2 Influenza Penn
Read more »
 COVID-19 pandemic has increased pregnancy complications and maternal death during deliveryCOVID-19 pandemic has increased pregnancy complications and maternal death during delivery Coronavirus Disease COVID Pandemic Pregnancy WomensHealth JAMANetworkOpen BIDMChealth harvardmed BrighamWomens HarvardChanSPH
COVID-19 pandemic has increased pregnancy complications and maternal death during deliveryCOVID-19 pandemic has increased pregnancy complications and maternal death during delivery Coronavirus Disease COVID Pandemic Pregnancy WomensHealth JAMANetworkOpen BIDMChealth harvardmed BrighamWomens HarvardChanSPH
Read more »
