Managing emotions better could prevent pathological aging UNIGEnews NatureAging
); denoised EPI data were co-registered to the anatomical T1 volume; the anatomical T1 volume was segmented and the extracted parameters were used to normalize all EPI volumes into the Montreal Neurological Institute space. This procedure was performed using FSL and SPM12.MRI scans were acquired at the GIP Cyceron using a Philips Achieva 3T scanner with a 32-channel head coil.
Quality control and preprocessing were conducted using statistical parametric mapping software on MATLAB 2017 . Before preprocessing, we manually centered the images to the AC-PC axis, realigned the functional and anatomical MRI images and then realigned all images to the last version of the SPM anatomical template.
The different regressors were then convolved with a hemodynamic response function according to a block design for univariate regression analysis. To account for motion confounds, the six realignment parameters were added to the matrices, and low-frequency drifts were removed via a high-pass filter . The final first-level matrix consisted of 2 sessions of 21 regressors each . Additionally, we addressed the influence of remaining motion on BOLD data by performing data censoring as described by Power and colleagues. Specifically, during the estimation of beta coefficients for each regressor of interest, volumes with FD > 0.5 mm were flagged in the design matrices and ignored during the estimation of the first levels.
For the second-level analyses, we used flexible factorial designs where the estimated parameters from first-level contrasts of interest were entered separately for each participant. The second-level design matrix was generated with SPM12 and included 12 regressors of interest .
Australia Latest News, Australia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
Utility of Wrist-Wearable Data for Assessing Pain, Sleep, and Anxiety Outcomes After Traumatic Stress ExposureThis cohort study evaluates whether wrist-wearable devices can provide useful biomarkers for recovery after traumatic stress exposure.
Read more »
 What is the impact of antibiotic exposure on the risk of inflammatory bowel disease?What is the impact of antibiotic exposure on the risk of inflammatory bowel disease? Gut_BMJ nyugrossman IcahnMountSinai antibiotics antibiotic IBD inflammation inflammatoryboweldisease disease
What is the impact of antibiotic exposure on the risk of inflammatory bowel disease?What is the impact of antibiotic exposure on the risk of inflammatory bowel disease? Gut_BMJ nyugrossman IcahnMountSinai antibiotics antibiotic IBD inflammation inflammatoryboweldisease disease
Read more »
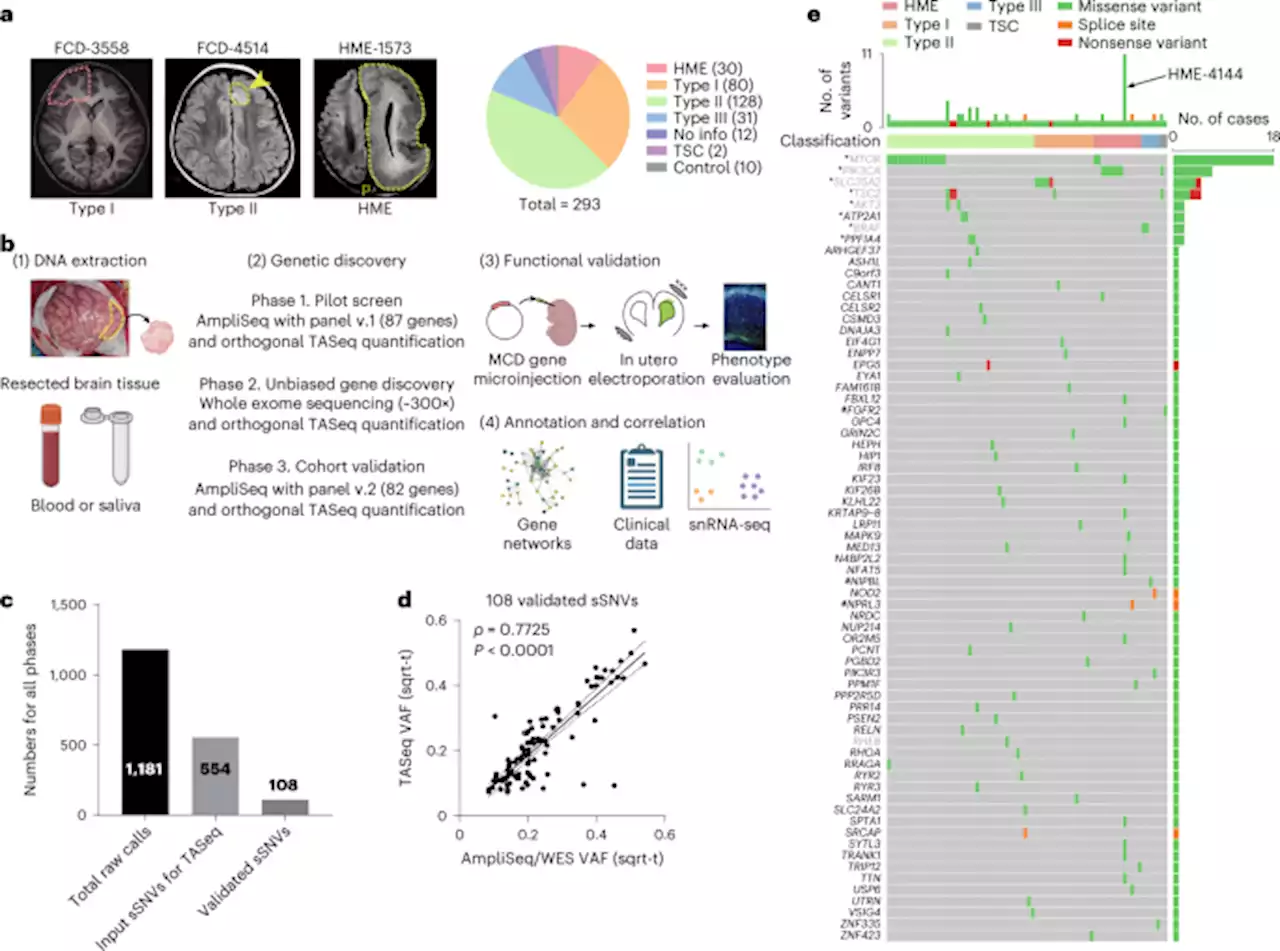 Comprehensive multi-omic profiling of somatic mutations in malformations of cortical development - Nature GeneticsThis Brain Somatic Mosaicism Network analysis of 283 cases of malformations of cortical development identifies 69 candidate and known genes in 76 patients. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing and mouse modeling implicate radial glia and daughter excitatory neurons.
Comprehensive multi-omic profiling of somatic mutations in malformations of cortical development - Nature GeneticsThis Brain Somatic Mosaicism Network analysis of 283 cases of malformations of cortical development identifies 69 candidate and known genes in 76 patients. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing and mouse modeling implicate radial glia and daughter excitatory neurons.
Read more »
 Sustainable Farnham house unites contemporary architecture and natureA sustainable Farnham house in the Surrey countryside combines a secluded, sloping site with modern materials
Sustainable Farnham house unites contemporary architecture and natureA sustainable Farnham house in the Surrey countryside combines a secluded, sloping site with modern materials
Read more »
 Gut microbiota of the young ameliorates physical fitness of the aged in mice - MicrobiomeBackground Aging is a natural process that an organism gradually loses its physical fitness and functionality. Great efforts have been made to understand and intervene in this deteriorating process. The gut microbiota affects host physiology, and dysbiosis of the microbial community often underlies the pathogenesis of host disorders. The commensal microbiota also changes with aging; however, the interplay between the microbiota and host aging remains largely unexplored. Here, we systematically examined the ameliorating effects of the gut microbiota derived from the young on the physiology and phenotypes of the aged. Results As the fecal microbiota was transplanted from young mice at 5 weeks after birth into 12-month-old ones, the thickness of the muscle fiber and grip strength were increased, and the water retention ability of the skin was enhanced with thickened stratum corneum. Muscle thickness was also marginally increased in 25-month-old mice after transferring the gut microbiota from the young. Bacteria enriched in 12-month-old mice that received the young-derived microbiota significantly correlated with the improved host fitness and altered gene expression. In the dermis of these mice, transcription of Dbn1 was most upregulated and DBN1-expressing cells increased twice. Dbn1-heterozygous mice exhibited impaired skin barrier function and hydration. Conclusions We revealed that the young-derived gut microbiota rejuvenates the physical fitness of the aged by altering the microbial composition of the gut and gene expression in muscle and skin. Dbn1, for the first time, was found to be induced by the young microbiota and to modulate skin hydration. Our results provide solid evidence that the gut microbiota from the young improves the vitality of the aged. Video Abstract
Gut microbiota of the young ameliorates physical fitness of the aged in mice - MicrobiomeBackground Aging is a natural process that an organism gradually loses its physical fitness and functionality. Great efforts have been made to understand and intervene in this deteriorating process. The gut microbiota affects host physiology, and dysbiosis of the microbial community often underlies the pathogenesis of host disorders. The commensal microbiota also changes with aging; however, the interplay between the microbiota and host aging remains largely unexplored. Here, we systematically examined the ameliorating effects of the gut microbiota derived from the young on the physiology and phenotypes of the aged. Results As the fecal microbiota was transplanted from young mice at 5 weeks after birth into 12-month-old ones, the thickness of the muscle fiber and grip strength were increased, and the water retention ability of the skin was enhanced with thickened stratum corneum. Muscle thickness was also marginally increased in 25-month-old mice after transferring the gut microbiota from the young. Bacteria enriched in 12-month-old mice that received the young-derived microbiota significantly correlated with the improved host fitness and altered gene expression. In the dermis of these mice, transcription of Dbn1 was most upregulated and DBN1-expressing cells increased twice. Dbn1-heterozygous mice exhibited impaired skin barrier function and hydration. Conclusions We revealed that the young-derived gut microbiota rejuvenates the physical fitness of the aged by altering the microbial composition of the gut and gene expression in muscle and skin. Dbn1, for the first time, was found to be induced by the young microbiota and to modulate skin hydration. Our results provide solid evidence that the gut microbiota from the young improves the vitality of the aged. Video Abstract
Read more »
 Did asbestos exposure kill ex-Ravenscraig welder? Family appeal over cancer deathTHE GRIEVING family of a former burner and welder who died from asbestos cancer are appealing to his former co-workers to help them establish how he…
Did asbestos exposure kill ex-Ravenscraig welder? Family appeal over cancer deathTHE GRIEVING family of a former burner and welder who died from asbestos cancer are appealing to his former co-workers to help them establish how he…
Read more »
